Conceptual Framework for Asset and Liability Management
Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction.
Introduction
Research aim
Research objectives
Research questions
Background of the Topic
Rationale of the Study
Purpose of the Study
Background of Banks
Chapter 2: Literature Review
Afraid of Drafting Lengthy Dissertation Papers?
Submit a Remarkable Dissertation Paper by Availing Dissertation Help from Our Experts
Liquidity Risk
Currency Risk
Interest Rate Risk
Categories of Risk
Credit Risk
Market Risk
Operational Risk
Pillars of Asset-Liability Management
Asset Liability Management Organization
Asset Liability Management Information System
Asset Liability Management Process
Risk Measurement Techniques
Gap Analysis Model
Duration Model
Value at Risk
Simulation
Summary
Chapter 3. 29
Research Methodology
Introduction
Method outline
Research Onion
Research Philosophy
Justification for election of chosen Philosophy
Research Approach
Justification for the exercise of the selected Approach
Research Design
Justification for the election of the selected Design
Data Collection Procedure
Data Sources: Primary and Secondary
Data Techniques: Qualitative and Quantitative
Research Limitations
Time Horizons
Summary
Chapter 4. 36
Results and Findings
Introduction
Qualitative Approach
Importance of Assets and Liabilities Management in Banks
Risk management as a parameter in controlling the risk
Advantage gained from the application of assets and liabilities management
Analogy of Banks through Ratio Analysis
Summary
Chapter 5. 40
Data Analysis
Introduction
Analysis of the Ratios
Summary
Chapter 6. 50
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
Linking with the objectives
Linking Objective 1: To recognise the role played by asset and liabilities of international banking in accordance with Indian banks
Linking Objective 2: To analyse the importance of the managing asset and liabilities of International banking in Indian banks
Linking Objective 3: To identify the issues and risk associated with the asset and liability trend in Indian banking system
Recommendations
Future Scope of the Study
References
Appendices
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework for Asset and Liability Management
Figure 2: Assets and Liabilities Management Process
Figure 3: Research Onion
Figure 4: Types of Research Design
Table 1: Core Deposit to Total Assets of SBI
Table 2: Loan to Total Deposit of SBI
Table 3: Liquid assets to total assets of SBI
Table 4: Gantt chart
Table 5: Profitability Ratio
Table 6: Management Efficiency Ratios
Table 7: Balance Sheet Ratios
Chart 1: Profitability Ratio
Chart 2: Management Efficiency Ratio
Chart 3: Balance Sheet Ratios
Chart 4: Debt Coverage Ratio
Chart 5: Leverage Ratio
Assets and Liabilities Management is an extensive framework that measures, monitors and manages the various market risks of the banks that are related to liquidity, interest rate, foreign exchange, equity and commodity price risks of the banks (Mohohlo, 2008). Therefore the banks have to effectively plan their strategies in order to minimize the risks. The assets and liabilities management helps the management of the bank to make business decision in a more structured framework with focusing on the risks that are bestowed on banks. Asset and Liability management encompasses the management of assets and cash inflows for meeting the various obligations of the banks (Allayannis et al. 2009).
The following project has been conducted for analyzing and evaluating the assets and liabilities management process of International banking in context to the five major banks of India. The research work will provide guidance in evaluating and understanding the nature of assets and liabilities and its effects on the management of risks. The role and impact of assets and liabilities management will be assessed on the banks so that the performance and their cash flows of the banks can be analyzed and the mitigation of various risks will also be determined.
Assets and Liabilities Management Process
The research aim of the study is to analyse the asset and liabilities of five major banks of India, State bank of India (SBI), IDBI, ICICI, Punjab National Bank (PNB) and Axis Bank. Topic will involve analysis of the banking sector and managing the asset and liabilities class.The researcher has selected five major banks of India as the case study so that concept of comparison of international banking with Indian nationalised banks can be analysed in a better way and focussed way. With the help of various theories and frameworks , the researcher will be try to define the relationship between management of asset and liabilities of international banking system in relation with five Indian banks
According to the research objective, structuring of research objectives will be developed so that, further diffusion of the research topic can be taken into account. With the assistance of research objectives, the segmentation of the research topic will be helpful that will allow proper division of wide topic into applicable form. The draft of objective will enable in successful accomplishment of the research aim that, is mentioned below.
- To recognise the role played by asset and liabilities of international banking in accordance with Indian banks (SBI, PNB, ICICI, Axis Bank and IDBI)
- To analyse the importance of the managing asset and liabilities of International banking of Indian banks
- To identify the issues and risk associated with the asset and liability trend in Indian banking system
Research questions have been framed so that, the most suitable result can be chalked out in understanding the topic of the research work in a much appropriate and concise manner (Claessens and Van Horen, 2012). The questions that, are listed provide emphasis on the method of analyzing that can enable in gaining possible and relevant information as per the carried topic. Thus, the number of questions has been jotted down for the particular topics
- What are the norms followed while assessing the various asset and liabilities class in Indian banks in accordance with Indian banking system?
- What are the various issues and risk associated with the international banking system for Indian banks?
- What are the various asset and liability management model that help in measuring the risk?
- What are the suitable strategies to mitigate the risk in international banking system for Indian banks?
Therefore the above mentioned question will throw better image of the research topic along with better assemble of related data and information.
Assets and liabilities management is the centre behind carrying out this research work. DeYoung and Yom (2008), noted that asset and liability management is the procedure through which the banks can effectively manage their balance sheet in order to grant for surrogate interest rate and liquidity outline. The risk like credit risk, interest risk and liquidity risk can be acceptable through the effectively management of assets and liabilities (Berkman et al. 2009). An effective Asset Liability Management approach aims to control the volume, mix, rate sensitivity, maturity, quality and liquidity of assets and liabilities do that the bank can achieve a prearranged acceptable risk or reward ratio.
The concept of assets and liabilities management helps in developing the process that can be effectively applied in International banking for reducing the risk that can affect the nature and business of banks. Mitra and Schwaiger (2011), describe that the management of assets and liabilities helps in planning, acquiring and directing the flow of cash through an institution with giving due care on the level of risks that can be posed in the transaction of the banks. Therefore, assets liabilities management can increase and maximize the profitability of the banks and effectively manages the financial risk.
The basic cause behind choosing this specific topic is to analyze and evaluate the process of management of assets and liabilities of the International Banking in accordance with five banks of India that are SBI, Punjab National Bank, ICICI, Axis Bank and IDBI. The Assets and Liabilities management focuses on the risk that is faced by the banks due to disproportion between assets and liabilities and due liquidity problem and changes in the interest rates of the banks (Berger and Bouwman, 2008). The liquidity problem arises when the banks can not be able to meet their obligations by transforming their assets into cash. The interest rate obligation may arises when the banks borrow short term that may be fixed or floating in nature and lending long term which may affect their interest rate policy. Therefore the interest rate has to be carefully handled otherwise it can affect the net interest income of the banks.
Research Onion
The Assets Liabilities Management, act as function that helps the banks in planning their funding and capital requirements and planning of profit along with the projection of growth (Monfort, 2008). ALM can help the manager of the banks to associate with the proactive and forecast the changes. The liquidity and interest risks have to be managed by the banks through assets and liabilities management. The interest rate risk can be minimized through acquiring short term nature of loans and investment as it can eliminate the rate of interest risk (Bodnar and Schmid, 2008). Therefore the assets and liabilities can be helpful in attaining the better balance in terms of profitability and long term viability. Thus the banks has to focus on the effectively framing the assets and liabilities of International banking system so that the banks can reduce the probable risks.
The election of this topic will help to focus on the effectiveness of the assets and liabilities management on the business of banking system. Banks try to throw light on the approach of assets and liabilities management so that the emerging risk can be handled in order to maintain the cash flow effectively. The research aims to study the importance of assets and liabilities in helping the Indian banking system. The study has been conducted to know the cash inflows and cash outflows in the Indian Banking system and how properly the assets and liabilities can be helpful in controlling the flow of cash in the banks. The Assets and Liabilities management has been applied as a method to relate the assets and liabilities of the banks on the basis of expected rates of return of the banks and their pattern for expected maturity. The management of the asset and liability can help the bank in adjusting their liability in order to meet demands of loans, need of liquidity and safety requirements effectively.
The carried research work is based on the five major banks of India that are State Bank of India, Punjab National Bank, ICICI, Axis Bank and Industrial Development Bank of India. SBI is a multinational financial and banking service that is based in India. SBI has an asset of US $388 billion till 2013 and 17000 branches and comprises 190 foreign offices that make SBI the biggest banking company in India (rbidocs.rbi.org.in, 2014). PNB is also located in India that serve more than 8.9 crores customers. PNB has total branches of 6081and also involving five foreign branches too and 6940 ATMs. It has a asset size of US $6.6 billion by the end of 2012-2013. ICICI bank is the largest private sector bank in India. It has a total asset of US $99 billion in March 31, 2014. The profit after tax of ICICI amounts to US $1637 million for the year ended 31 March 2014. Axis Bank is the third largest private sector bank in India. Axis bank has a 2402 branches network with a 12922 number of ATMs . It has a total asset of US $56 billion and revenue of US $5.6 billion until 2012 (www.igidr.ac.in, 2014). IDBI Bank Limited is a financial service company that, is owned by the government of India. The total assets of IDBI are US $54 billion with revenue of US $4.7 billion by the end of 2013. Therefore, these all banks has been considered to carry out this research work.
Types of Research Design
According to Allen (2010), International Banking System increases the effectiveness of foreign capital through enhancing and improving and also the flow of capital. The emergence of assets and liquidity management of International Banking system has forced the Indian Banking sector to implement the ARM concept into their banking systems. The uncertainty of interest rates can become the cause for the movement in the internal rate of return of the banks. Therefore the banks have to take suitable measure to eliminate those risks. The risk of interest risk can give rise to risk of liquidity and risk of credit that can affect the business of banks. Therefore, the need of Assets and Liabilities Management can be felt so that, the arising risk can be monitored and controlled. As per Melnikov and Romanyuk (2008), the Asset and Liabilities Management framework resist on three major buildings that are assets and liability management organization, asset and liability management information and on the process of asset and liability management.
The conceptual framework helps in enumerating the list of important theories that can help in better understanding of the research topics. The Asset and Liability Management in context to International Banking System will be taken into account so that, the theoretical approach can be highlighted in a brief manner.
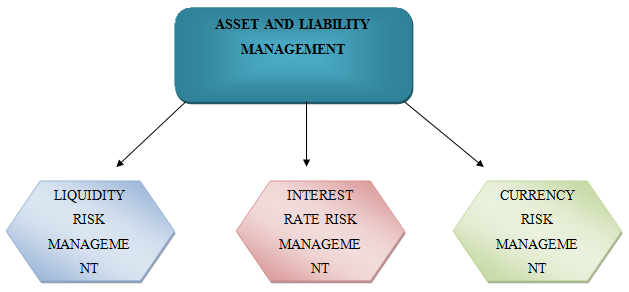
Figure 1: Conceptual Framework for Asset and Liability Management
(Source: Created by Author)
The above figure depicts that the assets and liabilities management can effectively manage and can control the risk so that the banks can do their transaction effectively. Therefore controlling those risks can bring development to the banks that can increase their growth and market expansion. The researcher can effectively analyze the asset and liabilities of the banks so that the topics can be analyzed more deeply.
The liquidity risk can arise in the banks through financing of long term assets by short term liabilities. Therefore, the liabilities need to be refinanced. The liquidity risk holds risk that, is related to funding risk, time risk and call risk (Entrop et al. 2008). The banks can have funding risk when the wholesale or retail outlets withdrawals the deposits without anticipation. The time risk arises when the assets of the banks converted into non-performing assets because of which, the expected cash flows are not achieved by the banks. The call risk is borne by the banks, due to precipitation of contingent liabilities and due to which the banks might not be able to capture the available business opportunities that are profitable.
Thus, the asset liabilities management helps the banks in managing the liquidity risk of the banks. The liquidity management helps the banks in gaining funds to check contractual or relationship constraints at affordable price at all times (www.bis.org, 2014). The liquidity management provide assurance to banks that they can effectively meet their liabilities whenever any due arises. The banks thus may need to undergo new transaction when needed that is the banks can collect fund from important clients.
In the words of Garleanu and Pedersen (2007), banks like PNB, ICICI, Axis banks can fall into liquidity risk when they may not be able to generate and cover their cash outflows due to insufficient availability of current assets and cash inflows therefore the banks can drop into the risk of liquidation. But according to Hibbeln (2010), the banks can plunge into liquidity risk if the higher interest rates of interest are offered by the banks on the deposits and deteriorating the quality of the assets, imposing high contingent liabilities and due to having delayed in the payment of the matured income. For instance, the Axis bank may be having a mismatch problem among the moderate life bonds and maturity arrangements of term deposits. Therefore Axis bank may need to float newer instruments having the shorter maturities so that the problem can be controlled and liquidity risk can be minimized effectively. Therefore, the banks can decline the liquidity risk through refinancing option, open market operations, etc.
Core Deposit to Total Assets of SBI
As per Ruozi and Ferrari (2012), the liquidity ratio of the State bank during the year, 2007 was 76.87%, which continuously decreased because of which the bank was not able to meet their requirements of operational and servicing needs. But after 2011, the liquidity position of SBI improved to 75.97. Therefore, further liquidity position of SBI can be understood by following below tables.
|
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
|
76.87 |
74.48 |
74.94 |
73.88 |
75.92 |
|
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
|
55.14 |
68.84 |
77.46 |
77.55 |
73.11 |
|
2007 |
2008 |
2009 |
2010 |
2011 |
|
8.55 |
9.02 |
9.17 |
9.35 |
10.83 |
According to data presented, the loan to total deposit increased was increased and almost stable in the year 2009 and 2010 from 2008. Therefore it can be analysed that the loan to total deposit of SBI does not represented better liquidity position from 2008 till 2010 as higher the ratio the banks liquidity position can become more weaker. The ratio of liquid assets to total assets has shown a increasing figure which depicts that the bank had a good performance in all these years. Therefore, it can be assed that the SBI bank in the year 2011 has effectively manage their asset and liability due to which they were able to strengthen their liquidity position and minimized the risk of liquidity too.
The banks can face the risk of foreign currency. The banks like ICICI and Axis Bank also operates in foreign countries. Thus, dealing in various currencies can bring risk to the banks. Therefore, these banks can focus on setting up limits and can carry active day time trading in order to minimize the currency risk (Hull, 2012). The banks such as ICICI, Axis banks, etc can follow value at risk approach for measuring the risk that can be attached with the forward exposures. The value at risk helps the banks in determining the probability of losses in bank’s portfolio that are based on the analysis of statistics of historical cost trends and volatilities.
Gatev et al. (2007) stated the fluctuations in the amount of investment of foreign currency or deposits can bring a risk to the earnings of the banks. The Asset and liabilities management policy helps in monitoring the unhedged foreign exchange risk in order to control the foreign currency risk. For example, if the ICICI bank holds a momentous amount of foreign currency liabilities, then the management of the bank has to measure and monitor the exposure of foreign currency on a continuous basis that can be helpful for the bank in estimating the fluctuations in the range of currency exchange.
As per Melnikov and Romanyuk (2008), the asset liabilities management policy requires that the banks has to be correlated the foreign currency deposits that are high in amount with the loans and investments in the same line of currency and with the equal term. For example, the Axis bank can eliminate the risk of foreign currency that is associated with the payments of interest by organizing the equal magnitude and timing of the flows of income by neutralizing the loans and investments of foreign currency. The bank has to consider the re-pricing terms that are offered and the availability of liquidity on the investment of foreign currency before providing any foreign currency deposits services to the clients located in other foreign countries.
Loan to Total Deposit of SBI
Kan and Smith (2008), stated that the policy of asset and management can effectively eliminate the unhedged foreign currency risk on material by implementing the external hedging instruments that is derivatives that can be also purchased by the banks. Banks like ICICI, Axis bank can use the financial derivatives in order to fence the balance sheet and effectively manage the risk of interest rate that can counterbalance the transaction costs of derivatives. Financial derivatives can be helpful to the private banks to eliminate the risk of foreign currency that can strengthen the cash flow of the banks.
Interest Rate Risk is the risk that can affect the profitability of the bank and their market value of equity when expected change occurs in the interest rate of the banks. If SBI makes changes in their interest rates then it can affect the price value of assets and liabilities. If the interest rate is excessive then it can pose a compelling threat to the earnings and the capital base of the banks whether it is Axis Bank, IDBI or PNB. The interest rate risk arises from various sources like basis risk, re-pricing risk, yield curve risk and option risk. Therefore the banks can effectively take cares these risks through effectively adoption of asset liabilities management (Allayannis et al. 2009).
The bank’s major business is related to taking deposits and lending capital to the clients and these activities of banks are exposed to interest rate risk (Hilli et al. 2007). The interest rate risk arises from re-pricing risk that born from the difference among the rate changes timing and timing of flow in cash. Basis risk that arises from the changeable rate correlation among the yield curves that affect the activities of banks, Yield curve risk that generate from the changing rate in the bounds of maturities and Option risk that is emerged from the interest rate related options that are attached to the products of the banks (www.communitybankingconnections.org, 2013). The assets and liabilities of the banks, get affected due to, noticing of change in the present value of future cash flow that implicates the risk on interest rate on the banks.
In the context of Petria and Petria (2009), the gradual stride of computerization in the banks and the devoid of total liberalism, the classic gap analysis are considered by the banks as a appropriate measure for identifying the interest rate risk on their business and transaction activities. Therefore the interest rate risk can badly affect the financial condition of the banks that can alter the net interest income of the banks and can decrease the earnings of the banks.
According to Severo (2012), the risk of interest rate in banks arises due to occurrence of mismatch between the deposits and loans of the banks. Therefore, the banks may need to systematically measure the risk of interest risk and banks may have to control the risk by thorough and correct management of assets and liabilities and matching it too. The Assets Liabilities Management policy helps in developing the boundary on the exposure of level of risk of interest risk that the banks might be predicting to follow. Therefore, the potential earnings of the banks can be affected due to changes in the interest rates of the banks.
Liquid assets to total assets of SBI
Romanyuk (2010), mentioned that interest rate risk has to be determined by the banks on quarterly basis. For illustration, suppose IDBI is having fixed loan and deposits more than 12 percent of total amount of assets has to measure the risk of exposure on the basis of monthly or weekly in order to know the degree of interest rate risk and their affect on the income of the bank.
Banks (2013), illustrated that the interest rate risk can be controlled and measured and monitored by the banks by number of methods and techniques like gap analysis, method of the duration gap, method of basis point value and the mechanism of simulation.
Credit is the risk of loss that originates when the obligor’s are unable to pay its obligations to banks. For example Punjab National Bank can fall into credit risk if the customers fail to make payment due on the credit card, mortgage loan; etc then the PNB can face a problem of credit risk. Therefore the PNB in order to reduce the credit risk, the bank can perform a credit check on the respective borrowers of credit. The banks can mitigate the risk through the adoption of risk based pricing, covenants, credit derivatives, etc in order to reduce the credit risk. Therefore asset liability management can control the credit risk by tracking the customers’ transactions and their accounts (Claessens and Van Horen, 2012). Credit Risk Management can also help the banks in measuring and reporting the regulatory mortgage risk assessment of a bank portfolio.
As per Godlewski (2006), the credit risk of a portfolio of banks lies on the following two factors:
External Factors
The external factors are related to the state of the economy, foreign exchange rate, rates and interest rates, trade restrictions, economic sanctions, policies of government, broad fluctuations in the prices of commodity or equity of the banks. These all factors can give rise to credit risk on the part of banks (Tran, 2010).
Internal Factors
The internal factors are borne by the banks due to their administration or policies of loans, improper structure of lending limits for loans or credits, insufficiency in the evaluation of borrower’s financial position, excessive inclination on collaterals and deficient risk pricing, inexistence of mechanism for loan review, etc. This can lead to the generation of credit risk in the activities of the banks that can affect the assets and liabilities of the banks (www.bai.org, 2014).
Gande (2008), elaborated that the credit risk of the banks such as SBI, PNB, Axis Bank, IDBI and ICICI bank can be measured by various methods. The methods, are related to analysis of ratio of non-performing advances to total advances, ratio of losses of loan to reserves of bad debt, determining the ratio of loan losses to the capital and reserves, provisions of loan loss ratio to flawed credit and the ratio related to provision of bad debt to total income. Therefore, the above mention banks can effectively analyse the level of credit risk by evaluating and analyzing the different mechanism to control credit risk.
Gantt chart
Market risk compromises of commodity risk, interest rate risk, forex rate risk, equity price risk and liquidity risk. The market risk can affect the operation of banks. Therefore, market risk management has to be adopted by the banks in order to manage their assets and liabilities. The assets and liabilities management can help the banks in analyzing the market risk so that it can be minimized (Mohohlo, 2008). Therefore, the banks can identify foreign exchange risks factors that can pose impact on the banks that can be helpful in stabilizing and improving the financial performance of the banks.
As opined by Campbell (2007), the market risk is concerned with the financial condition of the banks that arises from the detrimental flow in the market prices. The four main elements that are related to market risk are interest rates, currency exchange rates, and investment costs in trade portfolios and the exchange commodities prices in context to the activity of banks. The market risk affects the financial instruments of the individuals as well as the portfolio instruments.
Operational risk can be faced by the banks due to rise of monetary losses that may arise from the insufficient and failed internal processes, people and external factors. External events like natural disaster can bring losses to banks that can affect the physical assets of the banks. Therefore operational risk management can be followed by the banks by adopting good management information system and effective contingency planning (Berger and Bouwman, 2008). The banks can enhance their operational risk management through adopting new Basel Accord for setting operational risk. Therefore this approach can be helpful in reducing the operational risk capital need. The new capital regulations can make the banks to effectively control and manage the operational risk that can enhance the growth of the banks and easy flow of transactions. Therefore for example banks like SBI, IDBI; etc has to develop certain specific policies for tracking the product or an activity in order to mitigate the operation risk (Mitra and Schwaiger, 2011). The governing board of directors of SBI and IDBI has to figure out the operational risk as an important concern and should develop internal processes for timely reviewing, the strategy of operational risk. The SBI or IDBI will have to express monitoring and tracking system for exposing the operational risk and also the losses that may arise from the lines of business of banks. Internal auditing, by the SBI and IDBI can be enforced for chalking the policies and procedures for managing and mitigating the operational risk.
Country Risk
The country risk is associated with reference to investing in foreign country. The country risk holds the risk of political risk, exchange rate risk, economic risk, transfer risk and sovereign risk. As per, Amenc et al. (2009), the country risk can reduce the expected return of the banks on an investment. For example, if the ICICI bank makes a larger term investments or direct investments then the bank may have to face higher country risk that can affect the foreign currency earnings of the bank. Therefore, the ICICI bank may have to assess the country risk for evaluating the risk in relation to the repayments of liability by the borrowers of a foreign country. Gregory (2010), pointed that the ICICI bank may need to adopt internal audit function for scrutiny, the policies and procedures and active internal control like lending and marketing function for minimizing the country risk and effectively doing the business overseas. Thus, management of assets and liabilities can be successfully implemented in ICICI bank for balancing the cash inflow and cash outflow.
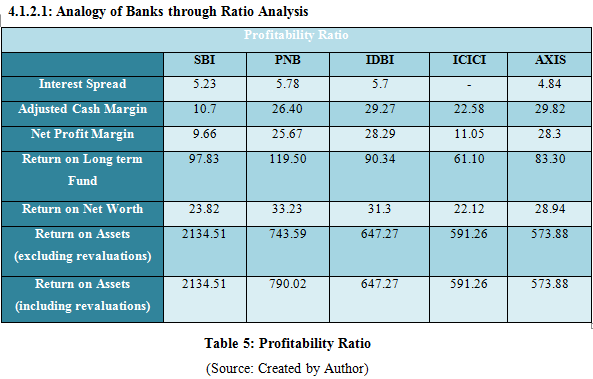
Profitability Ratio
Reputation Risk
Reputation Risk is referred as the current and expected indirect risk that, is concerned with the earnings and capital of the banks which is perceived by the customers, shareholders or regulators of the banks. The bank can face the reputation risk due to less compliance of banks with the regulatory standards and the industry service standards. Van Ness (2009), stated that banks like IDBI can have the reputation risk if the bank is unable to deliver the commitments to the customers that the bank may have made and due to lack of friendly relationship with the customers. This can affect the income and liability of the IDBI. Therefore, the bank may have to build the strategy that can increase the image of the bank among the customers.
Other author Hassett (2011) stated that the bank can have reputation risk if the bank does not follow the fair market proceedings. Thus, the bank has to harmonize with the expectation of the customers in order to deliver best service and gain high reputation. Therefore, high reputation of the banks can help in managing the assets and liabilities of the banks and maintaining a good balance, in terms of cash outflow and capital inflow of the bank.
Business and Strategic Risk
The bank can have a problem of business risk due to occurrence of alteration in the environment of business of banks which can largely affect the business decisions of the management of the banks (Coleman, 2007). For instance if the business risk prevail in the Punjab national banks then the bank earnings may get deploy and which can also affect the total capital of the bank and the assets and liabilities of the banks. Therefore effective assets and liabilities management can help in minimizing the business and strategic risk.
The ALCO committee includes the senior management of the banks that are, Chief Executive officer that helps the bank in building strategy for the banks and the budget of the banks and helps in deciding the risk management techniques for banks. The ALCO helps in making decision on behalf of banks for planning their balance sheet by taking account the prospective risk and making strategies for managing the interest risk and liquidity risk (Gatev et al. 2009). The purpose of ALCO can be discussed as:
Treasury Risk Management
The ALCO helps in providing recommendations on the Treasury Policy Statement and also review so that better decision can be taken by the management of the banks. Therefore careful monitoring by ALCO assists in set policies and limits for controlling treasury risk (Jorion and Khoury, 2010). ALCO scrutinize the treasure dealing strategy fixed for Treasury Risk Management.
Managing the asset and liabilities
The ALCO review and manages the alteration that occurs in the balance sheet of the banks like ICICI or Axis Bank. ALCO takes care of the structural changes and success of the strategic objectives. Thus provide recommendations on the kinds of products and treasury instruments in relation to the relevant duration and interest rate so that the overall balance sheet structure of the banks can be effectively managed (Cummins et al. 2010).
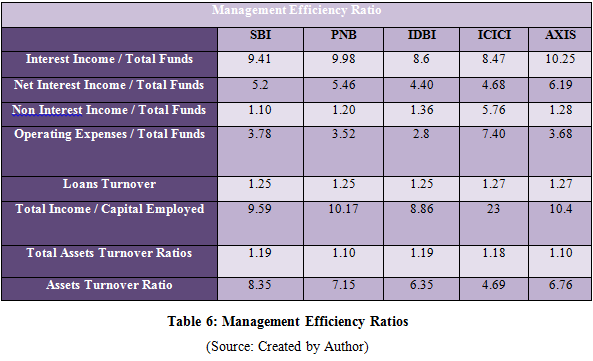
Management Efficiency Ratios
Interest Rate Risk and Hedging Action
The ALCO monitors the interest rate risk in adherence to Treasury Policy Statement. The ALCO make implementation of interest rate derivatives in the control of interest rate risk and also comprising periodic re-establishing to the portfolio of interest rate derivatives. According to Al-Tamimi and Al-Mazrooei (2007), ALCO also audit the percussion of basic risk on the net interest margin of the banks and suggest mitigation techniques to control the risk. ALCO envisage the necessary actions that to be taken on un-hedged positions and adopting the natural balance sheet hedges with respect to equity release swaps. But as per Rawls and Smithson (2009), ALCO takes the note for managing the market value risk and earnings risk in accordance to the allowed interest rate view and analyzing the impact of initial prepayments and their influence on the market value and earning risk on the activity of banks like SBI, PNB, etc.
Treasury Credit Risk
ALCO recommends changes to banks that might occur in the Treasury Policy Statement in relation to the credit and counterparty risk that might be faced by the banks. As per, Froot et al. (2008), ALCO also focuses on the limits of the country, instrument limits, high exposure caps, counterparty ceilings and review these limits in order to have better control on the risk of treasury credit. When existing counterparty does not fulfil the requirements of the Treasury Policy Statement then ALCO can suggest the possible actions that can be helpful in sorting out the problem in relation to various banks.
Funding
ALCO takes the work of reviewing the sources of funding, classify and determine the impact of new area of funding and analyse the changes in funding sources and the limits of funding for consenting with the Treasury Policy Statement (www.frm.reply.eu, 2014). The ALCO determine the balance among the funding and lending program of the banks for ensuring that the lending plan works in accordance with the funding plan of the banks. The cash flow positions of the banks are also reviewed by the ALCO in order to know the impact of the inflows and outflows of capital on the liquidity of the banks such as IDBI, PNB, etc.
Net Interest Margin and profit performance
ALCO measures the interest rate margin and predicted position of the banks and the variances that arises from the expected net interest rate margin by the banks (ideas.repec.org, 2014). ALCO assess the impact that takes place due to changes in the liquid assets market value, derivatives on the net interest margin of the banks, reserves and their profits too (www.bis.org, 2014).
This system enables the bank to compile the information correctly and purposefully. The better information system provides good assistance to the management of the banks to have a clear picture of the balance sheet of the banks. The information helps in analyzing and figuring out the financial risk that, can be effectively noted so that it does not affect the transaction of the banks and better decision can be taken too in relation to that (cab.org.in, 2014). Many Indian private banks like ICICI and AXIS banks have completely undergone with the system of computerization in their various branches that are helping in successfully integrating the treasury, forex and lending categories of banks. Therefore asset and liabilities are effectively managed through the initiation of information technology in various institutions of the banks that helps in quick transmit of information that provide quick assistance to the management of banks to make decision (Gregory, 2010). Through the implementation of information technology the costs related to holdings, trading and transactions are significantly reduced that provide support to asset and liability management of the banks. Banks like SBI, PNB has started the electronic fund transfer system carrying of securities through demat have helped these banks in managing and controlling the asset and liabilities of the banks that can reduce the financial risk of the banks. Therefore collection of information, storage and retrieval of information through the use of information system in the banks has brought positive change in the management of asset and liabilities of banks like SBI, IDBI, PNB, ICICI and AXIS banks.
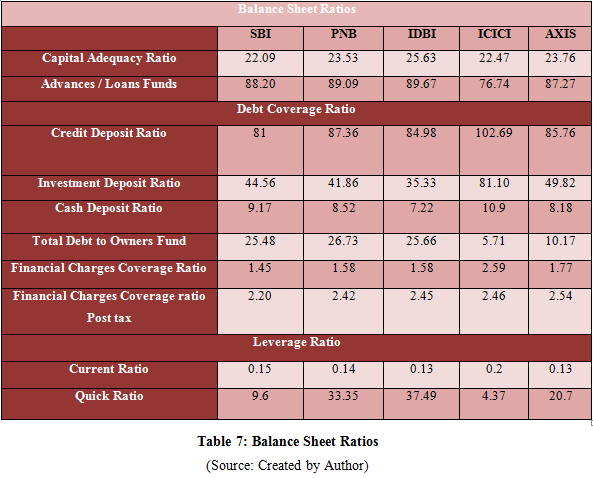
Balance Sheet Ratios
According to (Soumaya, 2012), stated that the information system in the banking sector helps the banks in facilitating decisions on number of issues like:
1. Helps in determining the major sources of capital such as core deposits, certificates of deposit and call financing.
2. Provide assistance in the minimizing the difference that arises among rate sensitive assets and rate sensitive liabilities of the banks in accordance with the certain amount of risk attached to assets and liabilities.
3. The problem related to the liquidity of the banks can be effectively avoided. For example ICICI bank’s liquidity issue can be controlled by decreasing the maturity mismatch between the assets and liabilities of the banks.
4. Information system can be beneficial in taking account of important factors such as size and duration so that the funds and capital of the banks can be effectively managed.
Figure 2: Assets and Liabilities Management Process
(Source: Romanyuk, 2010)
The primary Asset Liability Management processes holds the parameter that identifies measures and manage the risk. The first stage helps in developing up the Asset Liability Management function in the banks that helps in structuring the framework of bank measurements. Therefore the management of banks can focus on the parameter of risk measurements. The appropriate specification should build upon violability in the operation environment, availability of auxiliary data, availability of the expertise in the market and expected market and industry growth, etc (Memmel and Schertler, 2011). Therefore these parameters should notice the risk on the profitability of the banks and long term growth risk. The market value of portfolio equity can be helpful in measuring the risk that is associated with balance sheet of the banks. The Net Interest Income of the banks can also measure the balance sheet risk in relation to accounting year’s profit that arises from cash flow divergence in the accounting period.
There are number of factors that are used in measuring the exposure of banks to various risks:
In the words of Obstfeld (2010), gap analysis is a considered as technique for managing asset and liabilities that can be applied for assessing the risk of interest rate and liquidity of the banks. Therefore, it measures the control and degree of mismatch in asset and liabilities via either maturity gap or funding. The gap analysis is evaluated for assets and liabilities of varying maturities and is estimated for a fixed time frame. As per Khoury and Chan (2008), the model of gap analysis analyzes the re-pricing gap that can occur in the interest revenue acquired by the bank’s assets and the interest funded on the liabilities of the banks over a specific time or period. Thus, it focuses on the net interest earnings exposure of the banks with accordance to modifications in the interest rates in distant bucket of maturity.
Sercu et al. (2009), discussed re-pricing gaps is evaluated for, the assets and liabilities of banks having diverse maturities. If the gap is positive then it indicates that the assets of the banks is re-priced ahead of liabilities and banks can increase the net interest income if there is increase in the future rate of interest and if the gap is negative, it indicates that before re-pricing assets, the liabilities of the banks get re-priced. Sercu et al. (2009), stated that the manager of the banks has to consider at the rate sensitivity of every assets and liability on the balance sheet. The formula that can be use by the banks is as:
Debt Coverage Ratio
Net interest Income = Interest Rates Impacting Assets and Liabilities (Book Value of Rate Sensitive Assets – Book Value of Rate Sensitive Liabilities)
Therefore, the banks can identify the change in the interest rate that can affect the net interest income of the banks. For instance, IDBI bank can be benefited if the rate sensitive assets, is greater than the rate sensitive liabilities and due to rise in the interest rate. The negative gap that arises due to high rate sensitive liabilities over rate sensitive assets can be advantageous to bank during the time of decreasing interest rate. Therefore, the IDBI can reduce their risk interest rate if the bank analyzes the gap is around zero between asset and liabilities.
Duration is regarded as the crucial measurement of the interest rate sensitivity of assets and liabilities as the duration takes hold of the cash flow’s period of influx and the maturity of assets and liabilities (www.econ.ucsb.edu, 2014). Duration Model, is considered as the weighted average period to maturity of the total present value of the flow of cash. Duration analysis is taken by the banks for analyzing the elasticity of the market value of the bank’s instrument in compliance with the interest rate.
As per Kohn (2010), the higher the amount of duration, the price of the assets and liabilities can be more sensitive as per the changes in the rate of interest rate. The banks can effectively concentrate on the market value of their assets and liabilities through following the duration model. Therefore, the banks can evaluate the average life of the assets and liabilities. The Duration Gap, can be calculated as:
DGAP = DA – u DL
The DGAP highlights the difference of asset and liabilities cash flows timing whereas DA, is regarded as the average duration of assets and DL, is the average span of liabilities and u indicates the ratio of assets and liabilities. Therefore, the duration gap may help the banks in knowing the effect of high interest rate on the market value of the equities and on the predicted net interest income of the banks.
Rickards (2012) stated the value at risk is attributed to the maximum expected loss that a banks may have to face over a certain aimed horizon. The market risk of a portfolio of banks can be evaluated through calculating the net worth of the banks at a specific point of period so that the banks can focus on the risk that may have long-term impact. Therefore, the bank can make the decision effectively in the management of assets and liabilities so that the cash flows of the banks can be effectively managed. Thus, the market risk of the portfolio related to the assets and liabilities can be control by the banks and thus can reduce the mismatch between assets and liabilities of the banks.
Kusy and Ziemba (2010) opined that the Value at Risk can be also used by the banks in dealing with the other risks such as credit risk and operation risk. He has also mentioned that the larger the amount of value at risk, the banks can have higher risk on their number of portfolio. Therefore, the Value at Risk can be use for ranking the portfolios of risk in terms of degree of risk on each portfolio. Thus, the banks like IDBI, PNB, etc can assess their assets and liabilities for identifying there effect on the cash flows of the banks.
Leverage Ratio
In the words of Tolonen (2009), the model of simulation can help the banks in structuring a compelling aspect for analyzing the risk of interest rate and liquidity risk. The simulation technique, can productively manage the asset and liability of the banks.
Davis et al. (2011), mentioned that simulation model takes care of the following points:
- Shift in the absolute degree of interest rate
- Movement in the nonparallel yield curve
- Marketing strategies of the banks are under or over attained
- The margins earned by the banks in the previous period are not capitalized or improved
- Alteration in the funding mix of the banks
- Changes in the level of bad debt and prepayments
Therefore, these factors can help the banks in gaining correct information in controlling the assets and liabilities.
According to Rickards (2012), simulation model uses the power of computer to provide information about the cash flows and assets and liabilities to the management of the banks. Kohn (2010), analyzed that SBI or ICICI can generate accurate data and reliability through simulation on the prices, growth rates, reinvestments, etc under different scheme of interest rate and liquidity rate. Therefore, the banks can easily assess the possible effect of changes in the interest rate and liquidity risk on the earnings of the banks. As well as on the economic value and their affect on the cash flows.
Sercu et al. (2009), determined that the static simulation can help the banks in assessing the movement of cash that can arise independently from the current on and off balance sheet of the banks. The dynamic simulation can also assist the banks in having detailed information about the future course of action of interest rates and its affect on the liquidity position of the banks that can affect the business activity of the banks in managing assets and liabilities over the period. Therefore, the banks like PNB, Axis bank, and ICICI can use the simulation technique to balance their current earnings and potentiality of long-term earnings that can help them to maintain the adequate liquidity and interest rate risk exposures.
In the terms of Khoury and Chan (2008), the internal rating system can help the banks like SBI or Axis Bank in managing and controlling the effect of risks of interest rate, liquidity risk or credit risk. For example, the banks might be facing in their lending and other operational activities therefore, by managing and organizing the credit worthiness of the borrowers and the transactions qualities. Thus, the banks can maintain the level between assets and liabilities.
As analyzed from the study of the specific chapter, the researcher was able to acquire knowledge and details of the assets and liabilities management and the various elements of risk that can affect the assets and liabilities and cash flows of the banks. The different elements of risk like liquidity risk, credit risk and interest rate risk can their level of affect in balancing the assets and liabilities of the banks and on the earnings of the banks. The risk measurement techniques has been mentioned in this chapter that can provide assistance to the banks in lowering down the effect of risks from the bank’s asset and liabilities so that banks can manage it comprehensively. Analysis of risk helps the banks in successfully carry on with the activities of the banks. The gap analysis, duration model, value at risk and the simulation technique can be effectively evaluate by the banks for understanding the degree of impact of risk on the financial position of the banks like SBI, IDBI, PNB, ICICI and Axis Bank.
Research Methodology as a unit helps in the evaluating and determining the most probable approach that are required to be followed to accomplish the complete and detail outcome of the course.Bryman and Bell (2011), mentioned that the theories and concepts that are endorsed in the research methodology will assist in gaining the broad and better analysis of the research topic. Employment of research methodology helps in knowing the process adopted for analyzing the appropriate research of managing assets and liabilities and the measurement of risk for balancing the assets and liabilities. However, Crouch and Pearce (2012), pointed, that the brief procedure of research methodology can also guide towards the frequent errors that may generate limits within the process of research. Aloof from that, the researcher has tried to exercise each detail procedure of research methodology that can help and assist in superior analysis of banks of India and their relation with assets and liabilities management of international banking structure.
In the specific chapter, brief research methods for analyzing the assets and liabilities management superiorly and its affect on the various activities of the banks will be determined with reference to largest banks of India. The chosen research philosophy is positivism that can help in achieving information based on legitimate logic and evaluation. Further, deductive method will grant the researcher to develop the study based at the beginning on secondary sources that can help in describing the assets and liabilities management in the banks of SBI, ICICI, PNB, IDBI and Axis Bank. The descriptive design will guide the researcher in explaining the applied and followed concepts in the brief way that will further help in analyzing the impact of learning as well. Implementation of primary and secondary sources will provide great assistance and knowledge in a more detail manner of the research topics so that, good quality of analysis is followed.
Research Onion, is treated as a technique of methodology that helps in classifying the major segmentation of the research that has the capability for effectively analysing the topics. Brannen (2009), defined that the research onion is method that is helpful in doing the research process for the academic students in a structured format and by backing each segments of techniques will help in attaining results of the research process. Research onion, is grouped into six major segments that are philosophies, approaches, strategies, choices, periods, techniques and procedures.
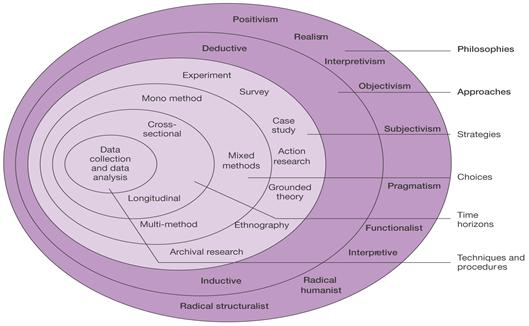
Figure 3: Research Onion
(Source: Saunders et al. 2009, pp. 52)
The above figured out diagram of research onion will help in understanding the each segments of research techniques so that, quality research can be carried for effective results.
In a research methodology, implementation of research philosophy can help the researcher in identifying the correct process for acquiring the brief about the research topic. Magilvy and Thomas (2009), discussed that the philosophy of research can help in examining the assumption process that is undertaken by the researcher while performing the research topics. However, the analytical process for checking out a particular topic can differ therefore; the implementation of research philosophy has to be in a proper and definite structure. Positivism is considered as a important part of philosophy.
Positivism as a course of philosophy guides in the appliance of logic that can assist in evaluating the concealed facts and information in an appropriate manner (Toloie-Eshlaghy et al. 2011). Although, positivism is controlled by scientific method, it works to eliminate the metaphysics so that, the brief observation and knowledge is effectively collected.
Positivism is followed in the current chapter that helps in better evaluation of the undisclosed facts and information that is related to the management of assets and liabilities in context to Indian Banks. Apart from that, significance of the study is time restrained because of which interpretative or realism study has not, been taken into account by the researcher. Therefore, the adoption of positivism philosophy controls the role of researcher in altering or evaluating the information that can lead to reduction of errors in the data as well.
An appropriate approach for the research work is needed so that, the structure required for developing the study is disclosed. A specific research topic has been follow for study under two broad categories either deductive or inductive. Inductive approach is regard as the study that helps in learning the research topic when the sufficient information on the chosen topic is not available. The early stage of inductive approach, comply with the observation that helps in generating the possible information that assists in building way for the research accordingly. However, Bergh and Ketchen (2009) stated that the inductive approach helps in structuring new theories for the related topics. Deductive approach is regarded as, the practical implementation of theories for effectively doing the research paper. Therefore, the approach of deductive aims to structure the theory in more specified and conceptualized manner.
In the are related to asset and liabilities management with the implementation of different theoretical knowledge. Models of assets and liabilities required an adoption of technique that can help in knowing in more definite and precise manner. However, as, no fresh concepts or theories has been applied by the researcher therefore, the approach of inductive tool has not been implemented in the current theory. Further, the role of assets and liabilities management in assessing the financial risk helps in understanding the nature of concepts in more structured manner.
As per, Cameron (2009), the research design comforts in briefing the framework of the research work and related topics that will benefit in choosing the most appropriate pattern for collection and analysis. A set of approach has been followed in the process of acquiring data that, helps in proper explanation of the research design. In academic research pattern, different types of research design are applied that, are exploratory, explanatory and descriptive.
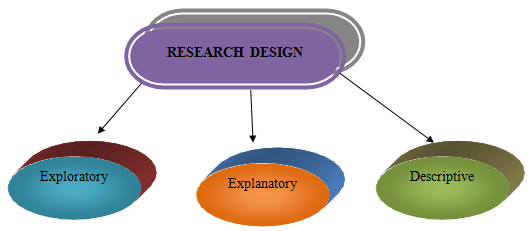
Figure 4: Types of Research Design
(Source: Crouch and Pearce, 2012)
Exploratory Design can help the researcher in addressing different varieties of thoughts and concepts that, can be used for completing the research work. In the words of Harrison and Reilly (2011), explanatory research design explains the existence of incidents or events and their effect on the research work. The last element of research design is descriptive design that, focus at generating details the reason of occurrence of events with correct description of the research topics.
Implementation of explanatory was not taken into account as the explanatory approach focuses on the concept of longitudinal study which was not appropriate for the particular research topics. Therefore, descriptive design is followed for the application of assets and liabilities management in the Indians banks for minimizing the potential risks that can affect the cash flows of the banks.
Magilvy and Thomas (2009), mentioned that the acquisition of data are helpful in figuring the correct and accurate results for the process of research work that can enable a standard design for conducting research work.
The sources of information are helpful in chalking out the research topic so that, better information can be extracted as per the requirements of the research topics. The primary and secondary are the two main sources of data that, are used in the research work as it provide helpful material in gaining information about the particular research topic. Crouch and Pearce (2012), illustrated that the primary data are helpful in assessing the raw data for implementing the information in the related research topic. Primary data are normally considered as first hand information therefore the researcher has to look that collected data are reliable and validate with the research topic. The secondary data in the particular research work are collected from various websites, blogs, journals, articles, magazines and literature source so that, the research topic can be explained in more brief and wider way.
Qualitative data can be used by the researcher as it can be helpful in presenting the researchwork and related topics in a more descriptive way that, can help the reader to understand the topic in much more easier and brief manner. et al. (2011), mentioned that the qualitative data provide theoretical concepts in the practical ground that helps in better understanding of the carried topic. Quantitative data on the other side follows the statistical data that can help the researcher in reporting the data of larger sample sizes. Both qualitative and quantitative approaches, has been effectively applied for analyzing the level of risk and their impact on the assets and liabilities of the banks.
According to Cooper and Schindler (2010), the research study can also have to bear some of the restriction that can be related to the concerned topic in the research work that might be avoidable or non-avoidable. In the particular work of research, the limitation that arises in the research work are:
Reliability: The method of data that has been applied for gathering the information was not able to provide consistent result. Therefore, the absence of reliability in analyzing the risk related to assets and liabilities management somehow affected the findings of the research work’s topic.
Time-Constraint: The researcher was bounded with the time that, provided shorter span of time for conducting the research work. The study of the topic in a deeper form was not achieved that, affected the research work.
Budget-Restrain: Due to availability of limited budget, the researcher has faced certain limitations in the learning of research topic. The researcher was not able to apply SPSS software due to insufficient finance that could have enhanced the quality of the research work (Bryman and Bell, 2011).
Most of the research topics are based on the characteristics of longitudinal or cross sectional that depend on the apportionment of time for conducting the particular topic of the research work. In the current research, adoption of cross sectional study has been implemented that has defined time period therefore, employment of “Gantt Chart” has been considered for the realization of the research work in simpler form. Saunders et al. (2009) illustrated that Gantt chart assist in segmenting the major work in accordance to the body of the study and helps in better close of the topic.
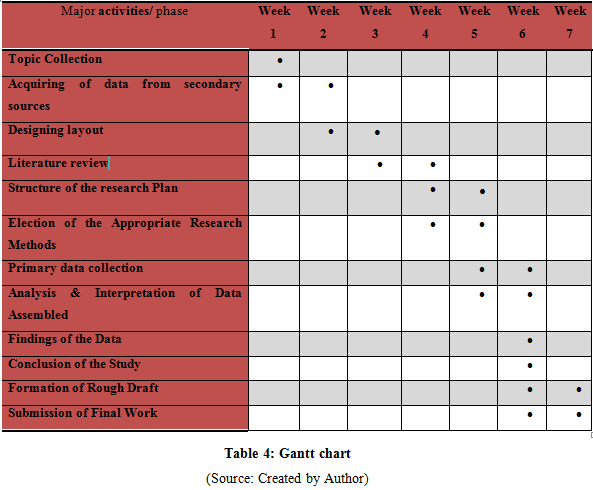
The carried chapter focus on the different techniques of research of selection that provide assistance in analyzing the topic in better an appropriate way. The current chapter has provided support to the researcher for coordinating the essence of the study with the applicable tools of research so that the perfect research methodology can be formed. The tools are more relevant to analyze the concepts of management of assets and liabilities for evaluating the different risk with reference to largest banks of India that is SBI, IDBI, Axis, PNB and ICICI.
In this chapter, the researcher has focused on the analysis of the data on the management of assets and liabilities of the international banking module in the banks. With the support of qualitative and quantitative analysis, the analysis of the information aids the researcher to enhance the quality of the information and analyze and conclude the particular topic in better way through better analysis. Kohn (2010), discussed that the data analysis helps the researcher in enforcing the theoretical knowledge in the practical application. However, Allayannis et al. (2009), pointed that the data analysis helps the researcher in analyzing the data that involves complexities and the drawbacks along with the data manipulation, limits of genuineness and other factors. Thus, a procedure of cross check has been formed via evaluation of data in the particular research work. The management of assets and liabilities in accordance with the international standard system will be evaluated in the following chapter with the help of calculated data. The data that will be generated in the particular chapter, the researcher will try to acquire knowledge in relation to the topic and will significantly recognize and analyze the findings so that valid points can be added in the process of collection of necessary data.
The qualitative section comprises the banks as the potential sample as the detailed concepts of assets and liabilities management has been applied to Indian’s bank. Moreover, the learning of qualitative will provide deeper analysis for every sub heading in more effective diffusion of the study topic.
The assets and liabilities management techniques has been considered by banks in order to improve and enhance the quality of the assets and assess the potential risk that are associated with the assets and liabilities of the banks that can affect the earnings and cash flows of the banks. The assets and liabilities management will help the bank in identifying the risk that can affect the short term profits, the long term earnings and sustenance scope of the long run of the banks. Thus, the assets and liabilities management model can help in maintaining the severe impact of risk on the earnings of the banks.
Risk management can be used as tool in the banks for mitigating the risk that are related to risk of development, operations risk, sales and marketing risk and future growth risk. Therefore the risk management can be effectively applied in the banks for managing the potential risk. The banks like SBI, ICICI and Axis bank has many multiple sites and also operating internationally. Therefore, the banks may not be able to control the risk effectively. Thus, the implementation of risk management can help the banks in knowing the risk that can have affect on the earnings and cash flows and on the balance sheet too.
Assets and liabilities management positively influence the income and cash flows of the Indians banks and recognizing the risk like credit risk, liquidity risk effectively which improves the performance of the banks and controlling the risk effectively has improved and strengthen their balance sheet. The credit risk management like risk rating, risk pricing and portfolio management has helped in managing the assets and liabilities which has helped the banks in attaining the long term goals of controlling the cash flow and assets and liabilities.
For gauging the performance of the Banks in accordance to the assets and liability management, the profitability ratio, management efficiency ratio, and different balance sheet ratios has been used for evaluating the same.
As concluded in the study, the research work throws light on the bank’s cash flows through management of assets and liabilities. The whole chapter on the chosen topic covers the aspects of knowing the performance of the banks in relation to assets and liabilities management through various important ratios. As realized from the primary research, the impact of assets and liabilities management is positive on the financial position and the cash flows of the banks. The study of the chapter explains the affect of assets and liabilities on the financial ratios of the banks.
The particular chapter will help the researcher in understanding the nature of ratios that has been calculated in the chapter four. The analysis of data has been done in this particular research work that helps in evaluating the effect of assets and liabilities management on the interest rate, credit rate, liquidity rate, cash flows and on the balance sheet of the banks. The ratios have been evaluated in this specific section that will help the researcher and readers to understand the current position of the banks. The ratios that has been determined, the profitability ratio, management efficiency ratio, and various balance sheet ratios have been analyzed in order to receive better result about the bank’s performance in relation to management and control of assets and liabilities.
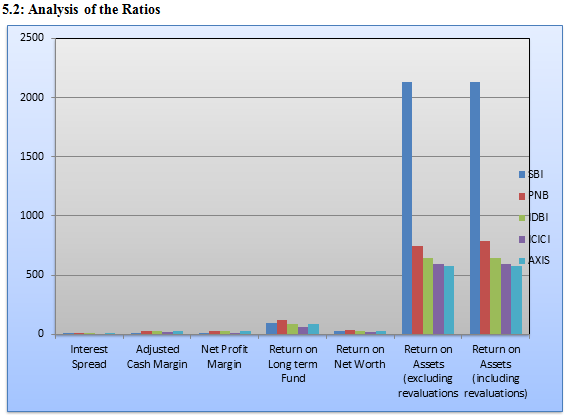
Chart 1: Profitability Ratio
(Source: Created by Author)
The interest rate spread ratio PNB is high followed by SBI, IDBI, AXIS and ICICI. Therefore it indicates that the PNB is able to generate more earnings that help them to effectively manage the difference between assets and liabilities. Thus, other banks have to monitor the change in interest rate spreads for managing their earnings. The net profit margin of IDBI is quite high in comparison to public banks of SBI and PNB whereas, between the private banks ICICI and AXIS, Axis bank has the better net profit margin which reflects that IDBI and AXIS has increased their sales that reflects on their profit. The adjusted cash margin is high for IDBI followed by PNB and then SBI which shows that the banks were able to effectively convert their sales into sales for keep on operating. In private sector banks, both AXIS and ICICI has positive adjusted cash margin figure. The return on long term funds of PNB is 119.50%, SBI is 97.83%, IDBI is 90.34%, ICICI is 61.10% and Axis is 83.30. Therefore, it reflects that the banks have effectively made investment for the long term which has ensure higher operating profit. The Return on net worth for SBI is 23.82%, PNB is 33.23%, IDBI is 31.3%, ICICI is 22.12% and AXIS is 28.94%. Therefore, PNB and AXIS bank have higher ratio in the public and private banking sector but all other banks has positive ratio which shows that the banks have affectively utilised the investment of the shareholders in order to create the better returns for their banks and business operation domestically and internationally. Thus, the banks were able to minimize the risk of bankruptcy that has maintained the investment in the banks. Therefore, the banks have to determine the levels of debt in order to seek excessive returns for enhancing the bank’s performance. PNB has gained higher return from the adjustment of tax on the total net worth of the bank and the bank is effectively deploying the capital of the shareholders. Other public banks SBI and IDBI has also good ratio that are ensuring the banks are also gaining better return but less than PNB. In private banks, AXIS has better figure than ICICI. Therefore, all the banks have generated better return on the net income.
The return on assets by excluding revaluations of SBI is 2134.51, PNB is 743.59, IDBI is 647.27, ICICI is 591.26 and Axis Bank is 573.88. Therefore, it can be analyzed that the banks were able to utilize their assets effectively in generating income. From the figure it can be assessed that the Punjab National Bank and ICICI has better number in comparison to other banks. Therefore, it indicates that these two banks are low asset insensitive because of which they are able to use their assets to gain higher income. The return on assets by including the revaluations, the figure is equal for the SBI, IDBI, ICICI and Axis banks as the figure by excluding the revaluation from return on assets but PNB has an increasing figure of 790.02 which shows that the PNB earnings is much better than in comparison to other banks and it also depicts that the PNB performance is also high then SBI, ICICI, Axis bank and IDBI. Therefore, overall it can be analyzed that the Punjab National Bank is working effectively than the other banks in relation to the ratios of profitability. In the whole, it can be evaluated that the banks have effectively managed the assets and liabilities which have controlled their cash flows and income for decreasing the mismatch among the assets and liabilities.

The management efficiency ratio that has been calculated in above chapter helped in analyzing the efficient levels of the banks in apportioning the assets and liabilities for improving the profitability of the banks. The interest income to total funds for PNB and Axis bank is higher than SBI, IDBI and ICICI. The PNB has 9.98 and AXIS has 10.25% while that of SBI is 9.41%, IDBI 8.6% and ICICI has 8.47%. Therefore it indicates that the PNB and AXIS bank has generated more income in spite of change in the interest rate. The net interest income to total funds of PNB has 5.46% which is higher than SBI of 5.2% and IDBI of 4.40% in respect to public sector banks while AXIS bank has 6.19% in comparison to 4.68% of ICICI. Therefore, it indicates that the banks with higher ratio are able to comply with change in rate with the assets and liabilities that have maintained their cash flows effectively. The non interest income to total finds in public sector bank, that is SBI has 1.10%, PNB has 1.20% and IDBI has 1.36% and in private sector bank Axis bank has 1.28%% and in ICICI 5.76%. Therefore, it has been analyzed that the banks were least affected from the economic and financial market cycles that have improved the earnings of the banks. The operating expenses to total funds is also at positive side for all the banks which indicates that the assets and liabilities have been well managed to cover the expenses of operating that have ensured the banks to continue with their operation effectively in the domestic circle as well as in the foreign circle. The positive ratio shows that the company has effectively met the profitability from the investors. The operating expenses to total funds of SBI is 3.78%, Punjab National Bank is 3.52%, IDBI is 2.8%, ICICI is 7.40% and Axis bank is 3.68%.
The return on capital employed for SBI is 9.59%, PNB 10.17%, IDBI 8.86%, ICICI 23% and Axis bank 10.4%. Therefore the figure reveals that the banks effectively generated the earnings from the money invested. PNB and ICICI has higher ratio that means that they were able to gain more profits from the apportionment of capital in comparison to other banks. Thus, the investors have been effectively attracted to invest in the banks and providing better return. The loans turnover is almost same for all the banks SBI, IDBI, PNB, ICICI and Axis bank. Therefore it reflects that the banks were able to generate enough sales to pay off their debts which have helped in improving the cash flows of the banks. The total assets turnover ratio is also quite same for the banks at around 1% which reflects that the banks are not able to make the maximum use of the assets for increasing the sales and meeting the liabilities. Therefore the low total assets turnover ratio has affected the sale of the banks because of which the cash flows of the company can be affected that can result into misbalance between assets and liabilities. The ratio of total assets turnover of 1% reflects that the net sales of the banks are equal to the total assets for the year which means that the banks have used all their assets for meeting the sales. The assets turnover ratio is quite impressive for all the banks. The ratio of SBI is 8.35%, PNB is 7.15% and IDBI is 6.35% while that of private sector banks, ICICI has 4.69% and Axis bank has 6.76. Therefore, it can be clearly analyzed that the banks are efficient in effectively applying the assets in generating the sales and meeting the assets and liabilities comprehensively too. Thus, the ratio indicates that all the banks are able to produce more sales with the use of fewer assets that resulted into higher turnover ratio.
Therefore, after analyzing the management efficiency ratio it has been found that all the banks have moreover equal ratios. The performance of Punjab and National Bank and ICICI is quite better than the other banks as per the management efficiency ratio. The management of the banks have to analyze the efficiency in order to increase the productivity of the bank. The banks will have to effectively utilize their assets in order to increase the sale and revenue. The management efficiency ratio analysis depicts that the banks has a great scope in increasing their total income on the employed finance which will help in managing the assets and liabilities and controlling the cash flows that will enhance the operation of the bank in foreign market and in national market. All the banks, SBI, IDBI, ICICI, PNB and Axis bank have noticed improvement in their financial position through effective management of assets and liabilities.
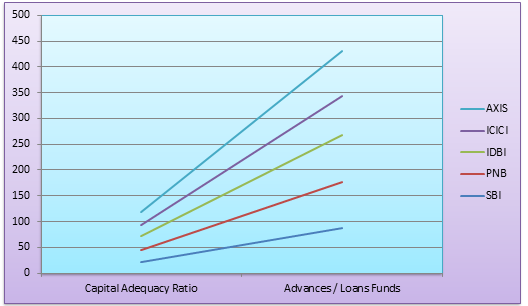
Chart 3: Balance Sheet Ratios
(Created by Author)
The analysis of the balance sheet ratios has helped in determining the financial health of banks that is SBI, IDBI, Axis, PNB and ICICI. The ratios have effectively identified the affect of assets and liabilities on the financial status of both private and public banks. The chart 3 comprehensively showcase that the banks performance is on increasing side. The capital adequacy ratio of SBI is 22.09%, PNB is 23.53%, IDBI is 25.63%, ICICI is 22.47% and Axis bank is 23.76%. Thus, it can be evaluated that the banks were able to maintain sufficient capital in order to control the losses that might arise due to various risk of interest rate risk fluctuation, credit risk and liquidity risk. Therefore, the positive capital adequacy ratio have influenced positively in enhancing and strengthening the balance sheet of the banks. Therefore maintaining the capital adequacy ratio has helped the banks in analyzing the risk and risk measurement techniques for reducing the affect of the risks on the earnings of the banks.
The advance to loan fund ratio of SBI is 88.20%, PNB is 89.67%, IDBI is 89.67%, ICICI is 76.74% and Axis bank is 87.27%. All the banks have higher advance to loan fund ratio that indicates the banks have taken borrow more money to finance their loans with a view to manage the assets and liabilities and the cash flows that can strengthen the balance sheet of the banks.
Therefore, both the ratios capital adequacy and advance to loan have effectively enhance the proficiency of the banks that helps the banks in managing the cash inflow and cash outflow for carrying out the necessary activities of depositing and lending.

The analysis of debt coverage ratio depicts that the banks are effective in generating income from their operations that are helping them to cap the payments of outstanding debts. The banks have generated the payment of loan from the borrowers on time because of which they were able to maintain their cash outflow and inflows. The credit deposit ratio of the banks is very high that indicates that the banks might not have sufficient liquidity to meet future unexpected requirements of fund. Therefore, it can be pointed that the banks have granted more money from the deposits. According to the ratio the PNB has lend more credit followed by IDBI and then SBI in public sector banks whereas in private sector banks ICICI banks has provided higher credit than AXIS bank from its deposits. The investment deposit ratio is also high for all the banks that represents that the banks have made high investment from the capital mobilised by them that shows that the banks has more cash outflows then cash inflows. SBI bank has invested more money than the Punjab National Bank and IDBI into projects from the cash acquired through deposits. As, in private sector again ICICI bank has contributed higher percentage of finance into ventures from the deposits than the investment made by AXIS bank. It can be regarded that all the banks have made investment that is positive sign that the banks are able to gain deposits so that they can lend credit and make investment effectively for the stability of cash flows and assets and liabilities too.
The cash deposit ratio is of all the banks is below 10% that represents that the cash balance held by the banks is very less in relation to the deposits. The total debt to owner’s fund ratio is high for all public banks SBI, PNB and IDBI and it’s less for private banks ICICI and Axis banks. Thus, it shows that the public banks are having more debt than the value of equity whereas the private banks have more equity then the amount of debts.Therefore it can be analyzed that the financial strength of the private banks are stronger than the financial position of the public banks. The financial charges coverage ratio all the banks are greater than the standard ratio of 1. Therefore, it can be depicted that the banks are able to pay off the financing expenses like interest or lease from their cash that helps in maintaining the cash flows and assets and liabilities and improving the financial strength of the banks. The financial charges coverage ratio post tax is also acceptable for all the banks that reflect that the banks are effectively covering of the requirements of obligations in spite of charge of tax. Therefore, the calculated debt coverage ratios shows that overall performance of the banks in generating income has improved due to which they are able to mitigate the limitations of managing assets and liabilities and the banks are capable to generate the returns on the capital and comprehensively deal with the emerging competition and risks. Thus, the banks are able to avail cash for covering the payments of debt that can be related to payment of interest or lease and payments of principle on debt. Other thing is that the banks can easily lend loan to the customers that can increase the income level of the banks.

The leverage ratio of the banks has been analyzed through the evaluation of current ratio and quick ratio. The leverage ratio of the banks depicts that the banks has higher assets than the level of debts. Therefore, it can be assessed that the banks are able to measure the risk effectively and cash flows. The current ratio that has been analysed shows that the all banks have somewhat similar figures. Therefore, it can be noted that banks were able to settle their liabilities and realized their assets effectively within 12 months due to management of assets and liabilities that improved their movement of cash flows. In public sector bank SBI has 0.15, PNB has 0.14 and IDBI has 0.13 current ratios while in private sector bank ICICI has 0.2 and 0.13 current ratio. The quick ratio of IDBI has better number of 37.49% than PNB that has 33.35% and SBI of 9.6%. In private bank AXIS has 20.7% and ICICI has 4.37%. Therefore, it can be evaluated that the banks are able to manage enough cash and other current assets for meeting the short term obligations and they are able to reduce the liquidity risk that helps in stabilizing the cash flows. As per the figure IDBI, PNB and AXIS banks are investing more resources in the working capital in order to gain profit.
Therefore, overall analysis shows that the Punjab National Bank is performing well in terms of profitability ratio and AXIS bank is doing better in asset turnover ratio, profits ratios and management efficiency ratios. ICICI bank has high current ratio in comparison to SBI, PNB, IDBI and Axis bank. Most of the banks are using re-pricing gap analysis and duration analysis to tackle down the risk related to interest rate risk, liquidity risk and credit risk. All the banks are effectively using interest rate derivatives for efficient management of position of assets and liabilities and flow of cash in business operation. Thus, all the banks are able to see improvement in their performance and earnings that are helping them to maintain balance between liabilities and assets and monitoring the probable risks and strengthening the balance sheet of the banks. Thence, asset and liability management are assisting the banks in the management of investments, deposits, credit, borrowing, FOREX reserves and capital and minimizing the gap among rate sensitive assets and rate sensitive liabilities and reducing the mismatch of maturity so that liquidity problem can be dodged.
Asset and liability management has emerged as a crucial activity for all the financial institution SBI, PNB, IDBI, ICICI and AXIS bank. All these banks are concentrating on effective management of assets and liabilities for improving and increasing the yield and reducing the exposure of risks. The result of this chapter shows that the public sector banks and the private banks both have a comfortable liquidity position of short term. Thus, public banks SBI, PNB and IDBI and private banks ICICI and AXIS bank both has a great scope to improve and enhance their profitability and income through making reduction in short term liquidity. Accordingly, the techniques of assets and liabilities management has helped the banks in tackling the risks of market effectively that improved their performance and earnings and it also helped to improve and stabilize the net interest income of the banks. Therefore, the banks can make effective decisions for guarding the level of risks that can affect the cash flows of the banks and balance sheet. Therefore, above all analysis presents that the banks performance have considerably improved.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusions
The whole research study was focussed on the concept of management of assets and liabilities in the Indian Banks and its impact on the earnings of the banks that is SBI, PNB, IDBI, ICICI and AXIS and reducing the affect of various financial and market risks. The study of the research paper shows that Indian banks are considered by the researcher so that the impact of assets and liabilities can be assessed. The effect of assets and liabilities management is positively related on the performance of the banks and controlling the risks and strengthening the flow of cash. The data acquired helped in knowing the level of success of asset and liabilities management on the balance sheet of the banks. It has been found that the banks have register growth in their performance and income that are positively affecting the cash inflow and outflow from the banks and recognize the possible risk.
On the basis of collection of data, the researcher will try to figure out the links generated between the practical applications and the objectives of the research work. As per aims of the research study, the researcher has focused to link the associated data so that the reliability and achievement rate of the study can be enhanced.
As observed in data findings and analysis, the role of assets and liabilities management is very effective on the performance of the banks that are positively influencing the balance sheet of the banks. Based on the survey, the researcher determined that all the banks SBI, IDBI, PNB, ICICI and AXIS bank are deeply concentrating on the management of assets and liabilities that are helping banks to mobilize their savings effectively. The banks are able to maintain the acceptable profitability and minimized the risk of interest risk and provided adequate amount of liquidity comprehensively as well. The role of assets and liabilities has made the banks to adapt to the changes that occur in the market in terms of risk. The net interest margin of the banks have considerably improved that have maximized their income by comprehensively quantify to the exposure to risk. Thus, the effective management of assets and liabilities helped the banks in managing the mix, volume, maturity, rate sensitivity, quality and the liquidity of liabilities and assets so as to receive a prearranged adequate ratio of risk or reward.
With the assistance of assets and liabilities management, it has been opined that the Indian banks are able to gain sufficient amount of earnings along with the better flow of cash both in domestic market as well as in foreign markets. Banks are productively adopting techniques of assets and liabilities and risk measurement techniques that are effectively minimizing the financial risk and market risk because of that the balance sheet of the banks are showing a better financial position of the banks. The assets and liabilities management has helped in minimizing the fluctuations in the returns of the banks due to change in interest rate and credit rate. Therefore, the liquidity and profitability of the banks have improved. Asset liability management has helped in planning, organizing and controlling the volumes of assets and liabilities and yields so as to gain the profitability levels through minimisation of interest rate risk. Thus, it can be linked that the banks can effectively anticipate the change in their returns through assets and liabilities management that can arise due to various risks. The banks can identify the sources of risk that can affect the balance between the assets and liabilities. The rate sensitive assets and rate sensitive liabilities are effectively measured by the banks.
The findings of the research work shows that the assets and liabilities of the banks are connected with various types of risk such as interest rate risk, credit risk and liquidity risk. There are also other types of risk like FOREX risk, currency risk, operational risk, reputation and country risk. Thus, these risks are influencing the net interest income and margin of the SBI, IDBI, PNB, ICICI and AXIS bank. Therefore, the banks have successfully adopted various risk measurement techniques to mitigate the effects of risks on the balance sheet and the cash flows of the banks. The gap analysis and duration analysis are used by the banks to measure the rate sensitive assets and rate sensitive liabilities and also the measurement of risks effectively. Thus, using the techniques for risk measurement has helped the banks in identifying the potential risk that are associated with the assets and liabilities and helped in measuring and stabilizing the cash outflow and cash inflow. Therefore, it has been linked that the Indian Banks are able to manage effectively the assets and liabilities that are strengthening the balance sheet and financial position of the banks.
Depending on the analysis and outcome of the research study, the researcher has enlisted some suggestions that can help in reducing the difference in the risks and management of assets and liabilities in Indian banks. As per the topic of the research study, the researcher has recommended certain norms that can help in better management of assets and liabilities in Indian Banks that can help in balancing the balance sheet and cash flows.
» The banks have to monitor and manage on continuous and regular basis the interest rate risk and liquidity risks that are associated with the balance sheet of the banks so that possible steps can be taken by the banks in controlling the risks. Therefore monitoring and managing the risks can help the banks in knowing the impact of the risks on the net interest income of the banks and on the liquidity of the banks.
» The banks have to keep in control the level of assets liability mismatch while expanding the range of the balance sheet. As large mismatch in the assets and liabilities can, result into volatility in the earnings of the banks. Thus, controlling the mismatch can strengthen the balance sheet of the banks and the banks can make suitable strategies so that they can be protected from the potential risks. Controlling the assets and liabilities can help the banks to face the financial risks effectively.
» The banks can follow the implementation of sensitivity analysis for the determination of management of risks. As, all the banks are considerably influenced by the interest rate risk. Therefore using the sensitivity analysis the banks can assess the risk and can take effective decisions regarding minimizing the risks. The sensitivity analysis can help the banks in analysing the risk associated with portfolios of the banks. Thus, the sensitivity analysis can help in measuring the impact of actual outcome on the performance of the banks in regard to the assumed outcomes of the banks.
» The banks should focus on strengthening the management information system and efficiency of computer handling so that the banks can accurately measure the liquidity and interest rate risks. The management information system can help the banks in faster flow of information so that the banks can make quick decision on the issues of risk and managing the cash flows.
» The banks has to take care of the effective management of cash balances and bank balances as it can fluctuate over the time so that the cash inflow and cash outflow of the banks can be controlled comprehensively.
» The re pricing gap analysis and duration analysis can be used by the banks for measuring the interest rate risk and liquidity risk for managing assets and liabilities in banks. The re-pricing gap analysis can help the banks in making differentiation among the interest rate gaps and liquidity gaps and the duration analysis can help in measuring the sensitivity of price of assets and liabilities in accordance to movements in interest. The use of interest rate derivatives can also help in managing assets and liabilities.
The scope of the research study was not successfully exploited to its maximum level due to presence of restrictions in the conducting study. In addition, the topic could have been explained better through analysis of more banks and using various risk measurement techniques in analysing and controlling the potential risks. Further, the study of comparative can also upgrade the chances of penetrating the different steps enforced in the management of assets and liabilities in the banks. The conducting the better study analysis of the income statement, profit and loss account of the banks can be assessed and the IFRS can be followed for the purpose of doing the research work in impressive way.
References
Allen, S.L. (2010) Financial Risk Management: A Practitioner’s Guide to Managing Market and Credit Risk, 4th ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley.
Banks, E. (2013) Liquidity Risk: Managing Funding and Asset Risk, 2nd ed. UK: Palgrave Macmillan
Berger, A. N. and Bouwman, C. H. S. (2008). Bank liquidity creation. Review of Financial Studies forthcoming.
Bergh, D. and Ketchen, D. J. (2009) Research methodology in Strategy and Management, 1st ed. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Ltd
Bryman, A. and Bell, E. (2011) Business Research Methodology. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press.
Cooper, D. and Schindler, P. S. (2010) Business Research Methods, 11th ed. London: McGra-Hill.
Crouch, C. and Pearce, J. (2012) Doing Research in Design - Page 68, 2nd ed. London: Bloomsbury Publishing Plc.
Davis, E., Coates, J. and Collier, P. (2011) Currency Risk Management in Multinational Companies. 5th ed. Hertfordshire, UK: Prentice Hall.
Dul, J. and Hak, T. (2012) Case Study Methodology in Business Research, 3rd ed. Oxford: Elsevier
Entrop, O., Memmel, C., Wilkens, M. and Zeisler, A. (2008). Analyzing the interest rate risk of banks using time series of accounting-based data.
Garleanu, N. B., and Pedersen, L. H. (2007). Liquidity and Risk Management. Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Gregory, J. (2010) Counterparty Credit Risk: The new challenge for global financial markets, UK: John Wiley and Sons Ltd.
Hassett, S. D. (2011) The Risk Premium Factor: A New Model for Understanding the Volatile Forces that Drive Stock Prices, New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons
Hibbeln, M. (2010) Risk Management in Credit Portfolios: Concentration Risk and Basel II, New York: Springer
Hull, J. (2012). Risk Management and Financial Institutions. New York: Wiley.
Jorion, P. and Khoury, S. J. (2010) Financial Risk Management: Domestic and International Dimensions, 2nd ed. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Blackwell Publishers.
Levi, M. (2010) International Finance. 5th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill Publishing.
Marrison, C. (2009) The Fundamentals of Risk Measurement, 3rd ed. New York: McGraw Hill.
Memmel, C. and Schertler, A. (2011). Banks’ management of the net interest margin: Evidence from Germany.
Mitra, G. and Schwaiger, K. (2011). Asset and Liability Management Handbook. London:Macmillan.
Mohohlo, L. K. (2008) Selecting and Managing External Fund Managers. In New Perspectives on Sovereign Asset Management, UK: Central Banking Publications
Obstfeld, M. (2010) “International Currency Experience: New Lessons and Lessons Relearned” Brookings Papers on Economic Activity.
Rickards, J. (2012) Currency Wars: The Making of the Next Global Crisis, USA: Penguin Group
Romanyuk, Y. (2010) Asset-Liability Management: An Overview, Bank of Canada Discussion Paper
Rosenberg, M. R. (2010) Currency Forecasting. 5th ed. Chicago, London: Irwin Professional Publishing.
Ruozi, R. and Ferrari, P. (2012) Liquidity Risk Management in Banks: Economic and Regulatory Issues, Italy: Springer
Saunders, M. N., Lewis, P. and Thornhill, A. (2009) Research methods for business students, Page 52, 5th ed. Harlow: Prentice Hall
Severo, T. (2012) Measuring Systemic Liquidity Risk and the Cost of Liquidity Insurance
Tolonen, Y. (2009) International mergers and industrial policy, 4th ed. Joensuu: University of Joensuu, Economics.
Tran, V.Q. (2010) Foreign Exchange Management in Multinational Firms. 5th ed. Michigan, USA: UMI Research Press.
Van Ness, D. R. (2009). Corporate Performance, 3rd ed. East Greenbush: Hallenbeck Publishing Co.
Allayannis, G., Ihrig, J. and Weston, J. (2009) “Exchange-Rate Hedging: Financial vs. Operational Strategies,” American Economic Review Papers and Proceedings, Vol. 91 (2), pp. 391–395.
Al-Tamimi, H. and Al-Mazrooei, F. (2007). “Banks' Risk Management: A Comparison Study of UAE National and Foreign Banks”. The Journal of Risk Finance, 8(4), pp. 394-409
Amenc, N., Martellini, L. and Ziemann, V. (2009) “Inflation-hedging properties of real assets and implications for asset-liability management decisions”. Journal of portfolio Management.
Barth, M. (2009). “Relative measurement errors among alternative pension asset and liability measures”. Accounting Review, pp.433-463.
Berkman, H., Bradbury, M.E. and Magan, S. (2009) “An international comparison of derivative use”. Financial Management 26 (4), 69–73.
Bodnar, T. and Schmid, W. (2008) “A test for the Weights of the Global Minimum Variance Portfolio in an Elliptical Model”. Metrica, 67 (2), pp. 127-43
Brannen, J. (2009) “Prologue, mixed methods for novice researchers: reflections and themes”, International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches, 3(1), pp. 8–12.
Cameron, R. (2009) “A sequential mixed model research design: design, analytical and display issues”, International Journal of Multiple Research Approaches, 3(2), 140-152,
Campbell, A. (2007). “Bank insolvency and the problem of nonperforming loans”. Journal of BankingRegulation, 9(1), pp. 25-45
Claessens, S., and Van Horen, N. (2012). “Being a foreigner among domestic banks: Asset or liability?” Journal of Banking and Finance, 36, pp. 1276-1290.
Coleman, L. (2007). “Risk and decision making by finance executives: a survey study”. International Journal of Managerial Finance, 3(1), pp. 108-124
Cummins, J.D., Phillips, R.D. and Smith, S.D. (2010) “The rise of risk management”. Economic Review, 83 (1), pp. 15–21.
DeYoung, R. and Yom, C. (2008). “On the independence of assets and liabilities: Evidence from U.S. commercial banks”. Journal of Financial Stability, 4, pp. 275–303.
Francis, J., (2010). “Portfolio analysis of asset and liability management in small-, medium-and large-sized banks”. Journal of Monetary Economics, 4(3), pp.459--480.
Froot, K.A., Scharfstein, D. and Stein, J. (2008) “A framework for risk management”. Harvard Business Review, 72 (6), 91–103.
Gande, A. (2008). “Commercial Banks in Investment Banking”. Handbook of Financial Intermediation and Banking, pp. 163-188
Gatev, E., Schuermann, T. and Strahan, P. E. (2009). “Managing liquidity risk: How deposit-loan synergies vary with market conditions”. Review of Financial Studies, 22, pp. 995–1020.
Gatev, E., Schuermann, T., and Strahan, P. E. (2007). “How Do Banks Manage Liquidity Risks? Evidence from the Equity and Deposit Markets in the Fall of 1998”. The Risks of Financial Institutions, pp. 105-132.
Harrison, R. L. and Reilly, T. M. (2011) “Mixed methods designs in marketing research”, Qualitative Market Research: an Int,ernational Journal, 14(1), pp. 7 – 26
Hilli, P., Koivu, M., Pennanen, T. and Ranne, A. (2007). “A Stochastic Programming Model for Asset Liability Management of a Finnish Pension Company.” Annals of Operations Research, 152, pp. 115-139
Kan, R. and Smith, D. R. (2008). “The Distribution of the Sample Minimum-variance Frontier."Management Science, 54 (7), pp. 1364-1380.
Khoury, S. and Chan, K. (2008) “Hedging foreign exchange risk: selecting the optimal tool”, Midland Corporate Finance Journal, pp. 40–52
Kohn, K. (2010) “Managing foreign exchange risk printability”. Columbia Journal of World Business, 25, pp. 203–207
Kouwenberg, R. (2010). “Scenario generation and stochastic programming models for asset liability management”. European Journal of Operational Research, 134(2), pp.279--292.
Kusy, M. and Ziemba, W. (2010). “A bank asset and liability management model”. Operations Research, 34(3), pp.356--376.
Magilvy, J. K. and Thomas, E. (2009) “A first qualitative project: Qualitative description design for novice researcher”, Journal of the Society for Paediatric Nurses, 14(1), pp. 298-300.
Melnikov, A. and Romanyuk, Y. (2008) “Effecient Hedging and Pricing of Equity-Linked Life Insurance Contracts on Several Risky Assets”. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Finance, 11 (3), pp. 1-29
Monfort, A., (2008) “Optimal Portfolio Allocation under Asset and Surplus VaR Constraints”. Journal of Asset Management, 9 (3), pp. 178-92
Mulvey, J. and Ziemba, W. (2008). “Asset and liability management systems for long-term investors: discussion of the issues”. Worldwide Asset and Liability Modeling, 10, pp. 3.
Oguzsoy, C. (2007). “Bank asset and liability management under uncertainty”. European Journal of Operational Research, 102(3), pp.575-600.
Petria, N., and Petria, L. (2009) “Operational Risk Management and Basel II”. Management and Economics, pp. 96-100.
Rawls, S. and Smithson, C. (2009) “Strategic risk management”. Continental Bank Journal of Applied Corporate Finance (Winter), 6–18.
Sercu, P. Uppal, R. and Hulle, C. V. (2009) “The Exchange Rate in the Presence of Transaction Costs: Implications for Tests of Purchasing Power Party” Journal of Finance, 50, pp. 1309-1319.
Soumaya, H. (2012) “The effect of debt, firm size and liquidity on investment -cash flow sensitivity”, International Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 2(2) 1-6
Stein, J. (2009). “An adverse selection model of bank asset and liability management with implications for the transmission of monetary policy”.
Toloie-Eshlaghy, A., Chitsaz, S., Karimian, L. and Charkhchi, R. (2011) “A Classification of Qualitative Research Methods”, Research Journal of International Studies, 20, 106-152.
Axisbank.com, (2014). Personal Banking | Internet Banking | Corporate, NRI Banking Services Online - Axis Bank. Available at: https://www.axisbank.com/ [Accessed 30th Aug. 2014].
cab.org.in, (2014) Asset Liability Management in Banks, Available at: https://cab.org.in/Lists/Knowledge%20Bank/Attachments/106/Assel__liability.pdf [Accessed on 22nd August 2014]
Icicibank.com, (2014). Personal Banking Services | Online Banking in India | Corporate Banking | Business Banking | NRI Banking.
Idbi.com, (2014). IDBI Bank.
ideas.repec.org, (2014) Currency Risk and Country Risk in International Banking.
Pnbindia.in, (2014). Welcome to Punjab National Bank.
Sbi.co.in, (2014). :: STATE BANK OF INDIA :: Safe Banking With SBI.
www.bai.org, (2014) Strategic Planning Meets Operational Risk Management.
www.bis.org, (2014) Basel Committee on Banking Supervision.
www.bis.org, (2014) Principles for the Management of Credit Risk.
www.communitybankingconnections.org, (2013) Effective Asset/Liability Management: A View from the Top.
www.econ.ucsb.edu, (2014) Value at Risk: Recent Advances.
www.frm.reply.eu, (2014) Specialised Risk Management and Measurement.
www.igidr.ac.in, (2014) Operational Risk Management in Indian Banks: Impact of Ownership and Size on Range of Practices For Implementation Of Advanced Measurement.
www.stat.berkeley.edu, (2014) Risk Measurement and Management.
Balance Sheet of SBI
Balance sheet of IDBI
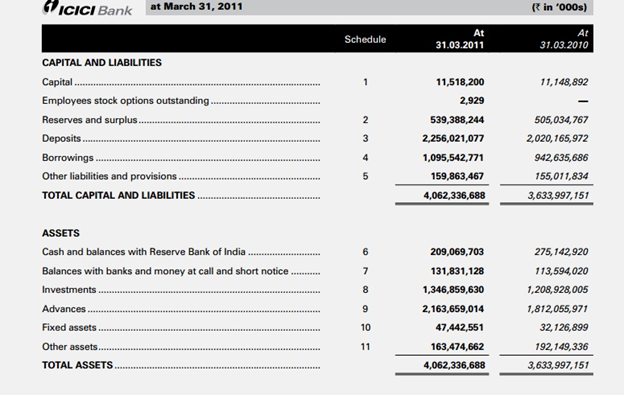
Balance sheet of ICICI Bank
Balance Sheet of PNB
Balance Sheet of AXIS bank
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2015). Analyze And Evaluate Asset And Liability Management Process Of International Banking In An Essay.. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/sample-dissertation-assets-and-liabilities-management.
"Analyze And Evaluate Asset And Liability Management Process Of International Banking In An Essay.." My Assignment Help, 2015, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/sample-dissertation-assets-and-liabilities-management.
My Assignment Help (2015) Analyze And Evaluate Asset And Liability Management Process Of International Banking In An Essay. [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/sample-dissertation-assets-and-liabilities-management
[Accessed 19 August 2024].
My Assignment Help. 'Analyze And Evaluate Asset And Liability Management Process Of International Banking In An Essay.' (My Assignment Help, 2015) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/sample-dissertation-assets-and-liabilities-management> accessed 19 August 2024.
My Assignment Help. Analyze And Evaluate Asset And Liability Management Process Of International Banking In An Essay. [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2015 [cited 19 August 2024]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/sample-dissertation-assets-and-liabilities-management.
