Describe about the Case Study of J Sainsbury PLC in International Business Environment?
This study reflects the analysis report of business environment of a specific company named J Sainsbury Plc. In this assignment, the business environment of the company Sainsbury PLC is analyzed with the respect of the some of the factors that includes the market structure, key responsibilities of the Sainsbury PLC etc. the impact of the international business environment on the environment of the business of the any marketers in corporate sectors. In the UK supermarkets, Sainsbury Plc faced lot of troubles from their key competitors such as William Morrison’s, TESCO, ASDA, etc. Following is the competitive environment analysis report of Sainsbury. Apart from that, this analysis report represent the market development and diversification along with market penetration with the help of Ansoff’s Matrix. For analyzing the internationalization drivers, this study displayed the analysis report using Yip’s Model.
Business environment is one of the vital part of the efficient and the effective management of doing the business (A Customer Churn Analysis Model in E-business Environment, 2012). The business environment determines the types of the business which will become successful in the environment (Krivogorsky and Joh, 2013). The business ms environment has the much more forces which shapes the segment of the business and also the product line.
This study firmly focuses on analyzing the background of J Sainsbury Plc and mission statement of the company. Apart from that, this study investigates the current supermarket industry in UK and describes the growth strategies as well as competitive environments of Sainsbury.
The organization Sainsbury PLC starts from 1869 by John James Sainsbury and his wife in London. It started in a small retail store and then it becomes the third largest of the retail stores of the U.K. it is operating more than the number of 1200 supermarkets in the world along with the numbers of the 165000 employees (J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015). It is now one of the listed companies of U.K. which is serving many of the customers on every day. It is mainly focuses on the customer satisfaction. It also tries to give the best experience of the shopping to its customers (J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015). It has its main focus on the creation of the loyal customers for the many years, by serving the customers rightly on the right time.

Figure 1: Logo of J Sainsbury Plc
(Source: J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015)
In the Drucker’s framework, the overall summary of the business model is created.
|
Options |
Description |
|
Strategic Plan |
The strategic plan of J Sainsbury Plc has a clear idea and long-terms strategy for achieving the vision and mission of the company (Valliere and Gedeon, 2008). |
|
Tactical Plan |
The tactical plan of J Sainsbury Plc is to become the most trusted retailers within supermarkets for the people in terms of shopping and working. |
|
Review and Control |
The company analyses market in order to understand the need and demands of people. The CEO of the company demands that they understand their customer better rather than other organization in supermarkets (J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015). |
|
Improvement plan and Unit Objectives |
The unit objectives of J Sainsbury Plc is to make customer’s live easier via providing the great quality of products and efficient service at a fair prices. Serve the customer according to their needs and demands. The improvement plan of Sainsbury is to introduce more glazing in the front of their store. It helps in maximizing the natural daylight. Moreover, Sainsbury plans to retain their existing front gable features (J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015). |
|
Individual Manager |
Sainsbury involve individual managers along with supervisor (J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015). The company divided the team and involved people within team according to skills and qualifications. |
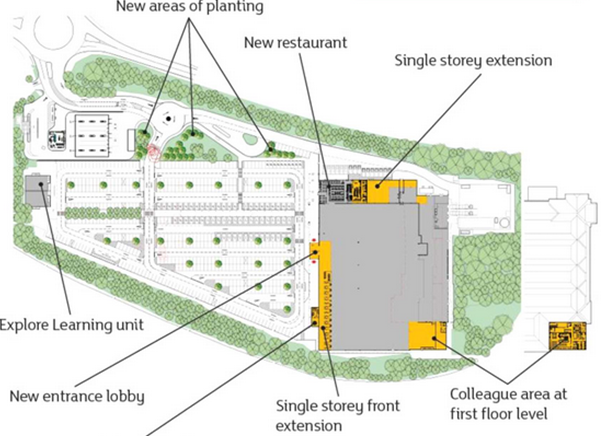
Figure 2: Improvement Plan of J Sainsbury Plc
(Source: J-sainsbury.co.uk, 2015)
According to Neupane (2015), the downturn of economic has had the long lasting effect on the UK supermarket industry. The revenue growth of UK super market is £162 billion. Apart from that the annual growth rate is 2.3 %. More than 61 companies runs their business within the super markets of UK and over 980990 employees works within the markets. The marketers of UK super markets allow the people to buy products with low price. Apart from that, supermarkets of UK sell products at a low profit margin. In order to get benefits from the poor economy conditions, the companies of supermarkets in UK sell their products in low profit margin (Vaughan, Yang and Tang, 2012). The market review report of 2014 displayed that a price war sparked by the company TESCO and Morrison’s through announcing of large price cut of products without decreasing quality of products as well as service. This war mainly happens with the Sainsbury and ASDA who similarly cuts their products and services price since last few years. It shows the negative influence on the revenue growth of supermarket industry. Therefore, it has been also seen that, the new entrants in UK supermarkets faced lots of competition from the existing businesses such as TESCO, ASDA, Sainsbury, etc.
|
Company |
Market Share |
|
TESCO |
29.10% |
|
ASDA |
17.12% |
|
Sainsbury |
16.60% |
|
Morrison’s |
11.00% |
|
Independent Companies |
2.00% |
|
Other Companies |
24.18% |
1. Introduction of the Company and Analysis of Mission Statement
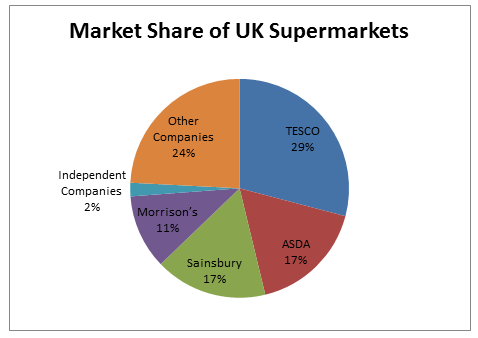
Figure 3: Market Analysis Report of UK Supermarket of 2014
(Source: Stern, 2014, pp- 127)
Porter Five Forces Analysis of Sainsbury Plc
Threats from New Entrants: In order to start the business within the supermarket in UK, organization has to invest more capital. Thus, the company is able to establish their products and service as well as build a success or string brand image. Due to high investment of capital, Sainsbury faced low threats from the new entrants. The main threats that have to faced by the company are existing brand. There are several companies such as Morrison’s, ASDA, TESCO, etc who are already established their brand. In the existing supermarket of UK, Sainsbury also established their name and along with the competitors, they service more than 85% of all shopping in the UK. On the contrary, Krivtsova and Belozerova (2013) cited that in the supermarket in UK, the new entrants have to make long term plan for starting their business along with the regulatory permission of government. It takes long time to execute. From this point of view, Sainsbury faced low competition from the new entrants. However, the superior policies such as low cost products, online shopping facilities, 24 x 7 complain help line, quick delivery of purchased products, etc helps in capturing the lot of loyal customer to Sainsbury Plc.
Intensity of competitive rivalry: Luck (2012) acknowledged that the intensity of rivalry within the supermarket of UK is extremely high for Sainsbury. There are several string brand name such as TESCO, ASDA, William Morrison’s who already established market in the retail industry of UK through high capital investment and strong strategies as well as policies. According to Mertens (2014), TESCO and ASDA always focus on switching the customers through effective service such as high quality products in low prices, promote the brand through effective media like Facebook, Twitter and involve film stars or sportsman in order to promote the brand. Earlier it has been analyzed that UK retain industry creates competition by decreasing product price itself that result low revenue growth. However, the major competitors, like TESCO, Waitrose have gained their revenue high in the slow growth market. It displayed that big competitors capture the loyalty of customers. Therefore, the competition from rivalry within the retail industry in UK is high. Apart from that, the other company likes ASDA, Lidl, etc continuously low down their products service price in terms of capturing high market share. This downturn gained 25% growth for those companies during the time of recession that occurs in 2008.
Threats from Substitutes Products: In the apparels items, Sainsbury faced high competition from the substitute products. On the other hand, in food items, the company faced low competition from substitute products. Regarding apparel products, there are wide ranges of counterfeit product development companies that decrease market share of luxury brands. The food items does not affected by the substitute products of Sainsbury because people of UK are very much conscious about their health.
Bargaining Power of Customers: In the retail industry in UK, lots of competitors are present with strong brand image. It indicates that customer have wide range of options in order to switching cost from one company to others. From the point of view of bargaining power of customer for Sainsbury, business is strongly high. People of UK are too much price sensitive. If they find similar products in other companies at low cost, they switch their mind and buy the products from that company.
1.1 Background of J Sainsbury Plc
Bargaining power of Suppliers: The positions of suppliers in UK retail industry are not string. According to Pophal (2014), majority of suppliers are fails to make loyal contract with the big brands in UK supermarkets such as TESCO, ASDA, Morrison’s. Due to this specific reason, suppliers have not string position within the retail industry in UK. Therefore, suppliers provide strong raw materials to the Sainsbury that is one of the greatest opportunities in making the company in top position. Moreover, bargaining power of the suppliers is relatively low for Sainsbury in UK retail industry.
Market Penetration: Holopainen and Toivonen (2012) depicted that some of the people gone for brand rather than products. Therefore, establishment of successful brand image can increase the products. Therefore, Sainsbury played the following activities in establishing their brand –
- Sainsbury started their market with a own website (j-sainsbury.co.uk) and own property in the supermarket in UK.
- Through advertising and involving sportsman and film stars, promote their brand. Apart from that, they serve leaflets in their stores in order to increase brand.
- In 2014, they increase 2.10% revenue itself
- They involve the club card scheme in their operation that is help in gaining more customer loyalty and represent a way of penetrating the market within the UK supermarket.
New Products or Service: According to Moussetis (2011), 25% of things depends of product development and service for any organization in supermarkets. Therefore, Sainsbury serves their customers with wide range of facilities such as insurance, saving scheme, credit card loans, life of the food, Mortgage, etc (Vörös et al., 2012).
The company includes the electronics products in terms of selling and works on it for improving the long life of electronics products.
It has been also seen that no other company in supermarket working on the mobile sector. However, mobile sector is one of the most fast growing industries now a day. Therefore, Sainsbury tries to introduce products of telecommunications such as mobile phone, smart watches, music devices, etc.
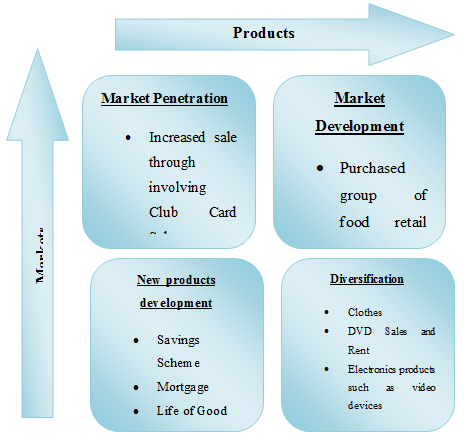
Figure 4: Ansoff’s Matrix of Sainsbury Plc
(Source: Zuba, Sekuła and Buczek, 2012, pp-121)
Market Development: After starting the business, Sainsbury continuously tries to increase their markets. Sainsbury purchased group of food retail chain that consisted of Quinnswotrth, Stewarts, and other products in the north region of UK (Zuba, Sekuła and Buczek, 2012). Apart from that, Sainsbury is joint venturing with the Casinos. This can helps in developing their products.
Products Diversifications: In the food and non-food retail sector, Sainsbury recently extended their market greatly. Sainsbury first started their business with grocery items and later frequently diversify their business into several areas such as clothes, customer financial services, internet services, DVD rent as well as sales, petroleum, etc. It helps Sainsbury in built their skills in the private labels Nakae (2012). Thus, the company recently runs over 1200 stores in all part of UK including high street and popular place such as London main town, University of London, etc.
Market Drivers: The company j Sainsbury Plc currently operates in the supermarket of UK. However, they continuously growth their market share in the retail industry in UK and examine the market in order to open new stores (Law, Lee and Yip, 2011). The company plans for overseas expansion on worldwide. However, it has been seen that majority of UK retails fails to expand their business worldwide. Several companies are able to established market successfully such as Dixons, TESCO, etc. In 2013, Sainsbury purchased a chain in United Sates as well as in Egypt in terms of expanding their business. Though, Sainsbury was unable to expand their business due to hut hard from the core domestic business (Li et al., 2011).
1.2 Analysis of the mission statement (Drucker’s Framework)
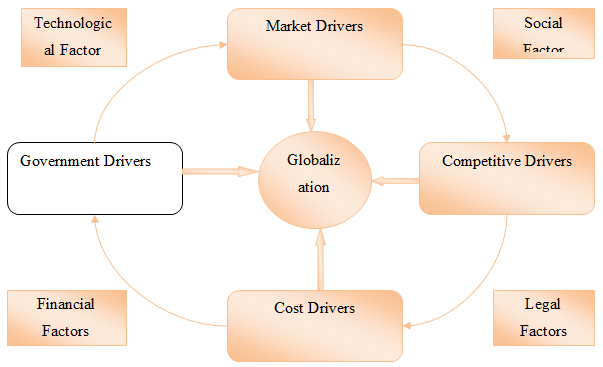
Figure 5: Yip Model
(Source: Moger et al., 2010, pp- 461
Furthermore, it has been also seen that Sainsbury embarking on the opening programme for increase the small stores in the UK retail industry. The Sainsbury Plans to open more than 50 convenience shops within the second half-financial year.
Cost Drivers: Sainsbury operates more than 1200 stores in all part of the UK. Due to low bargaining power of suppliers in the UK supermarkets, Sainsbury takes raw materials in low prices from the suppliers (Moger et al., 2010). The company also takes fresh food products from the farmer. The company make contract with the farmer and import the raw materials directly from them (Tsang, Yip and Lo, 2011). It not only helps in serving low price products to the customers but also make more customer loyalty via providing fresh food. Apart from that, Sainsbury started their business with partnership of Casinos. Thus, they earn more costs. However, Sainsbury increase 2.10% revenue growth of their business during the recession in 2008. It shows the effective cost drivers of the company.
Government Drivers: Sainsbury properly maintain the government liberalization of UK government. Apart from that, it has been identified that, Sainsbury faced troubles from the core companies in United State and Egypt. However, Sainsbury paid extra tax rate when they enter into the market of United State. Moreover, the communication of Sainsbury with the government of UK is good and the company certainly changes the rules and regulation according to the changes of governmental rules (Yip, Sun and Liu, 2011). Sainsbury paid governmental incentives fairly.
Competitive Drivers: Low product prices and quality of service is the key competitive advantage of Sainsbury. Since 1869, the company is implementing several policies and strategies in their business process that is creating competitive advantages in the retail industry in UK. Growth rate of Sainsbury Plc is also high (Over 1200 stores in super markets and more than 161000 employees work). Furthermore, the acquisition of the company for new stores opening is not flexible in the international market (Li et al., 2011).
Conclusion
This study analyzed the business environment of J Sainsbury Plc that is running successfully their business in UK supermarkets. In order to understand the better overview of the customers and their specific needs as well as demand along with to find out what the exact technologies needs to be used to serve the customers. This framework is known as the Drucker’s Framework. By describing the strategic plan process of the principles of the organization and through this it also analyze the mission statement. Analyst summarized the three questions in the three axes: the horizontal axis is positioned to the customers, an inclined axis on the applied technologies and the vertical axis on buying the needs. Sainsbury PLC has the great importance here with the great impact of the cultural environment. The importance of the international trade environment as well as with the great impact of some of the global factors of the Sainsbury PLC that is described with the concentration of the globalization. At last the policy and the relation of the Sainsbury PLC is represented with the reference of the particular policies.
2. Industry Analysis
Reference List
A Customer Churn Analysis Model in E-business Environment. (2012). JDCTA, 6(9), pp.296-302.
Alrawashdeh, R. (2012). The Competitiveness of Jordan Phosphate Mines Company (JPMC) Using Porter Five Forces Analysis. International Journal of Economics and Finance, 5(1).
Fogel, G. (2001). An Analysis of Entrepreneurial Environment and Enterprise Development in Hungary. Journal of Small Business Management, 39(1), pp.103-109.
Holopainen, M. and Toivonen, M. (2012). Weak signals: Ansoff today. Futures, 44(3), pp.198-205.
J-sainsbury.co.uk, (2015). J Sainsbury plc / About us. [online] Available at: https://www.j-sainsbury.co.uk/about-us/ [Accessed 28 Feb. 2015].
J-sainsbury.co.uk, (2015). J Sainsbury plc / Business strategy and objectives. [online] Available at: https://www.j-sainsbury.co.uk/about-us/business-strategy-and-objectives/ [Accessed 28 Feb. 2015].
J-sainsbury.co.uk, (2015). J Sainsbury plc / Business structure. [online] Available at: https://www.j-sainsbury.co.uk/about-us/business-structure/ [Accessed 28 Feb. 2015].
J-sainsbury.co.uk, (2015). J Sainsbury plc / Our values. [online] Available at: https://www.j-sainsbury.co.uk/about-us/our-values/ [Accessed 28 Feb. 2015].
J-sainsbury.co.uk, (2015). J Sainsbury plc / Store improvement plans. [online] Available at: https://j-sainsbury.co.uk/about-us/property/supermarkets/south-east/west-hove/plans/store-improvement-plans/ [Accessed 28 Feb. 2015].
Krivogorsky, V. and Joh, G. (2013). Comparative analysis of European corporate governance regulatory environment - recent developments. International Journal of Economics and Business Research, 6(4), p.419.
Krivtsova, M. and Belozerova, V. (2013). PORTER FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS ON THE EXAMPLE OF “MISS FITNESS” CLUB. Theoretical & Applied Science, 2(06), pp.81-86.
Law, Y., Lee, H. and Yip, A. (2011). Subspace learning for Mumford–Shah-model-based texture segmentation through texture patches. Applied Optics, 50(21), p.3947.
Li, J., Kushima, A., Eapen, J., Lin, X., Qian, X., Mauro, J., Diep, P. and Yip, S. (2011). Computing the Viscosity of Supercooled Liquids: Markov Network Model. PLoS ONE, 6(3), p.e17909.
Luck, D. (2012). CIM Coursebook 08/09 Assessing the Marketing Environment. Hoboken: Taylor & Francis.
Mertens, M. (2014). Controlling instruments in the "INTOP" business game. Munich: GRIN Verlag GmbH.
Moger, T., Haugen, M., Yip, B., Gjessing, H. and Borgan, Ø. (2010). A hierarchical frailty model applied to two-generation melanoma data. Lifetime Data Anal, 17(3), pp.445-460.
Moussetis, R. (2011). Ansoff revisited. Journal of Management History, 17(1), pp.102-125.
Nakae, A. (2012). Serotonin 2C Receptor Alternative Splicing in a Rat Model of Orofacial Neuropathic Pain. Neuroscience & Medicine, 03(01), pp.69-74.
Neupane, R. (2015). The Effects of Brand Image on Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Intention in Retail Super Market Chain UK. Int J Soc Sci Mgt, 2(1).
Pophal, L. (2014). The Everything Guide to Customer Engagement. Cincinnati: F+W Media.
Stern, J. (2014). Introducing competition into England and Wales water industry – Lessons from UK and EU energy market liberalisation. Utilities Policy, 18(3), pp.120-128.
Tsang, D., Yip, T. and Lo, I. (2011). Conceptual model and sensitivity analysis for simulating the extraction kinetics of soil washing. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 11(7), pp.1221-1233.
Valliere, D. and Gedeon, S. (2008). Application of physical science analysis to strategic management monitoring and control systems. International Journal of Business Environment, 2(1), p.50.
Vaughan, L., Yang, R. and Tang, J. (2012). Web coâ€Âword analysis for business intelligence in the Chinese environment. AP, 64(6), pp.653-667.
Vörös, T., Bazsó, G., Tarczay, G. and Pasinszki, T. (2012). Matrix-isolation spectroscopic and computational study of [2C, 2N, 2S] isomers: Photochemical generation of SCNNCS and NCSNCS from NCSSCN. Journal of Molecular Structure, 1025, pp.117-123.
Yip, T., Sun, X. and Liu, J. (2011). Group and individual heterogeneity in a stochastic frontier model: Container terminal operators. European Journal of Operational Research, 213(3), pp.517-525.
Zuba, D., SekuÅ‚a, K. and Buczek, A. (2012). Identification and characterization of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-nitro-β-phenethylamine (2C-N) – A new member of 2C-series of designer drug. Forensic Science International, 222(1-3), pp.298-305.
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing stye below:
My Assignment Help. (2016). J Sainsbury PLC: A Case Study In International Business Environment (Essay).. Retrieved from https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/a-case-study-of-j-sainsbury-plc.
"J Sainsbury PLC: A Case Study In International Business Environment (Essay).." My Assignment Help, 2016, https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/a-case-study-of-j-sainsbury-plc.
My Assignment Help (2016) J Sainsbury PLC: A Case Study In International Business Environment (Essay). [Online]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/a-case-study-of-j-sainsbury-plc
[Accessed 19 August 2024].
My Assignment Help. 'J Sainsbury PLC: A Case Study In International Business Environment (Essay).' (My Assignment Help, 2016) <https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/a-case-study-of-j-sainsbury-plc> accessed 19 August 2024.
My Assignment Help. J Sainsbury PLC: A Case Study In International Business Environment (Essay). [Internet]. My Assignment Help. 2016 [cited 19 August 2024]. Available from: https://myassignmenthelp.com/free-samples/a-case-study-of-j-sainsbury-plc.
